The more reliable it is to seal connections in the heating system. Choosing a universal and heat-resistant sealant for heating pipes
Extremely important point For high-quality installation heating system is right choice material for sealing threaded connections. This type of connection especially requires high-quality sealing. IN last years When installing heating systems, modern sealants based on heat-resistant silicone or a special Teflon thread are often used for threaded connections.
Unskilled or unscrupulous workers sometimes use materials that are not intended for this at all to seal connections in heating systems. For such work it is absolutely not suitable to use cheap silicone for plastic windows, since this material does not withstand high temperatures, and this always leads to a coolant leak.
The choice of the type of coolant also greatly influences the quality and operating features of the heating system. We suggest you understand these points, which are extremely important when installing heating systems.
Types of thread seals
Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of the most common modern seals for threaded connections of heating system pipes.
Tape Fum
Fum tape is made from thin fluoroplastic film and has good chemical resistance. Despite the popularity of this thread seal for fitting connections, this material still has significant disadvantages. Fum tape does not have sufficient adhesion to the surfaces being sealed, which negatively affects the sealing of the system. In addition, when the system changes in temperature, the tape often slips out of the thread gap, which also leads to leaks.
When using fum tape in connections with very smooth surface or a small thread gap at the time of assembly, it is squeezed out of the connection. Also, this sealant is not suitable for threaded connections of heating system pipes with a diameter of more than 25 mm.
Non-drying sealants
Non-drying sealants provide fairly easy and convenient work on sealing threaded connections of heating system pipes. Such thread seals are a very viscous paste-like sealant based on synthetic resins, fillers and oils. This seal is quite convenient to use, but is suitable only for use in non-pressure systems. It protects the thread surface well from corrosion and prevents joints from seizing during assembly. Installation of pipe connections using non-drying sealants is quite simple and convenient, well suited for pipelines with low environmental pressure.
Among the disadvantages of this type thread seals insufficient reliability of sealing systems with high pressure. In this case, the seal is gradually squeezed out of the threaded gap. This material does not have sufficient chemical resistance to aggressive antifreeze environments, which leads to leaks in the system.
Solvent-based sealants
Solvent-based sealants for heating system joints are typically used in combination with flax strands. This significantly reduces the costs of such a not very cheap sealant, but may affect the quality of the connections. Such thread seals are drying pastes. The use of such material in our country began relatively recently. Solvent-based sealants dry out on the inside threaded connection and become resistant to being squeezed out of the gap. They provide good lubrication of the connection threads and protect them from corrosion.
However, when using solvent-based sealants, it should be remembered that such a sealant may shrink after drying. Therefore, additional tightening of fittings may be required.
Teflon sealing thread
Teflon thread is synthetic fiber, which is impregnated with a special Teflon composition. It is easy to use and provides high-quality sealing of heating system fittings. Withstands high temperatures up to 120 o C. This thread seal is very popular for hot and cold water, in thermal and gas networks. Teflon sealing thread provides excellent protection inner surface fittings from corrosion. It is noteworthy that Teflon thread, unlike other types of seals, can be used on wet threads and when low temperatures air.
The disadvantage of such a seal is its poor chemical resistance to aggressive media of antifreeze for heating systems. The combination of these substances leads to the formation of heating system leaks.
Anaerobic gels
Anaerobic gels, getting into the narrow gaps of connections of heating systems in contact with metal and in the absence of oxygen, polymerize. In this case, neither shrinkage nor expansion of such a seal occurs. The resulting durable, solid, thermosetting plastic provides excellent sealing of heating system connections. It is noteworthy that anaerobic gels do not change their original liquid state when exposed to air for a long time. Thanks to this property of aerobic thread seals, clogging of the working channels and valve seats does not occur. Unhardened residues of the substance can be easily removed from the joint surface with a regular napkin.
The use of anaerobic gels in heating system connections simplifies the assembly process due to the lubricating properties of the material. This seal is resistant to high pressures, the quality of the seal does not depend on the twisting force. Anaerobes are characterized by a combination of excellent chemical resistance and low cost, which makes such seals quite popular in the installation of heating systems.
Disadvantages of anaerobic gels include their undesirability for connections larger than 4 inches in diameter. Such sealants are not recommended for use at low air temperatures, as this slows down their polymerization. You should also use anaerobic gels only on dry and clean surfaces.
Features of antifreeze in the heating system
Often, when installing a heating system, the customer expresses a desire to fill the system without plain water, but a frost-resistant coolant that does not freeze at low temperatures. This is quite convenient and justified for use in houses where periodic living is planned. When using antifreeze, there is no need to drain the coolant when the heating system needs to be stopped. long time in the middle of winter.
However, the use of frost-resistant coolants entails a number of features when installing and operating a heating system. When using antifreeze, special requirements must be placed on sealants and gaskets of the heating system. For example, rubber gaskets cast iron radiators under the influence of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze they will swell and lose their waterproofing properties. By by and large and heating boilers are not designed for the thermophysical properties of antifreeze. Experts do not recommend using such coolants, as the risk increases emergency shutdowns boiler from overheating or premature failure of heating equipment.
A competent combination of materials, methods of connecting pipes, coolant, heating equipment and qualified workers in the design and installation of the heating system guarantees its long and productive operation.
The radiator piping must include shut-off valves
We already know about that, but today we’ll talk about connecting heating radiators to pipes. In a heating system, threads are often used to connect elements. All equipment is installed on the circuit using threads. This is also an expanzomat ( metal tank with a rubber membrane inside), and a pump, and batteries, and the same meters. Metal lines can also be connected with threaded couplings. At the same time, there are different types of threads and methods of sealing connections. Let's figure out how to properly connect heating pipes to each other and to the batteries.
Types of carving
Steel pipes can be connected by welding or pipe thread. Connection of heating radiators to pipes is carried out only with metric threads, which are cut on the nuts. To assemble individual parts of a stainless steel metal line together, threaded connections of heating pipes are used, which are:
- conical (BSPT);
- cylindrical (BSPP).
In heating systems, conical threaded connections of heating pipes are used, and cylindrical ones are used only for drains. Cutting is carried out using a tool called a clamp. They are manual and electric. Hand tool consists of a handle, a ratchet and a head with cutting teeth. The presence of a ratchet allows you to work in hard to reach places, for example, in the section where the highway runs along the wall.
To cut a thread, you need to chamfer and treat the surface with oil. In the process of cutting threads on a heating pipe, oil must be added, this reduces friction and heating of the part. In order for the joint to be airtight after connection, it must be sealed. It is also compacted and metric thread on the nuts of all circuit elements.
Types of seals
Previously, there was not such a variety of seals as there is today. Some plumbers use the entire range of materials in their work, while there are conservatives who still recognize only linen. Are they right? Let's figure it out. How to seal the threads on a heating pipe:
- tape-fum;
- flax with paste;
- anaerobic adhesive sealant;
- sealing thread.
Flax was previously used in tandem with red lead, lubricant or oil paint. Today, a special sealing paste is used that prevents the flax from drying out and rotting.
Flax dries in systems with hot coolant, but rots in cold water. In the first and second cases, the result of the process will be the appearance of a leak. Thanks to the paste, the fitting can be loosened a little after twisting, turning back no more than 45 degrees. Universal material, suitable for connection metal pipes heating, and for polymers.
Flax is suitable for all types of threads on heating pipes, regardless of diameter. It is the cheapest of the seals. It is important to wind it correctly:
- using a metal blade or a file, notches are made on the thread;
- a strand of flax is rolled into something like a thread;
- winding is carried out as the fitting is screwed in (usually clockwise);
- The protective paste is applied evenly.
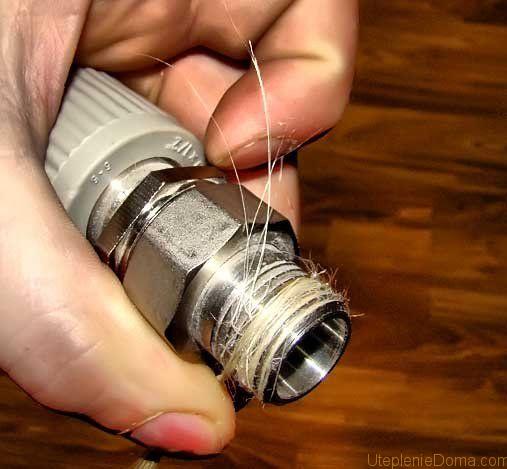

Sealing with flax
When winding flax, it is important not to overdo it. First you need to make the first turn, which will secure the seal to the thread. This leaves a tail. On the second turn, the remaining tail is picked up and wound together with the common fiber. Make sure there are no twists. The material should be distributed evenly along the threads from the end to the fitting body. When working with flax, when connecting heating pipes, you need to watch your hands, as they are constantly smeared with paste. If you take hold of it with such hands, an imprint will remain.
Fum tape is used for thin-walled fittings and connectors with fine threads. The material is easy to work with and your hands are always clean. At the same time, fum tape is quite expensive and is mainly used for small diameters. Significant disadvantage This seal is impossible to adjust. That is, if the joint of the heating pipes is twisted and needs to be loosened a little to center it, then the connection loses its tightness.
The sealing thread, like fum tape, does not require lubrication or the use of special paste. It can be wound onto dirty or wet threads and is suitable for plastic.
According to the characteristics stated by the manufacturers, the sealing thread can be turned away (adjusted) by 180 degrees.
Sealants are applied to clean and grease-free threads (usually new ones). They are:
- dismantled;
- difficult to dismantle.
But in fact, they are all not dismantled. Before connecting heating pipes using sealant, you must be prepared for the fact that it will be possible to disassemble the connection only after heating. And only then, perhaps, will it be possible to unscrew it. But during installation, the connection points do not even need to be tightened with wrenches.
Connecting the circuit and batteries
Let's start understanding the methods of connecting heating pipes to a radiator by considering the materials from which heating systems can be made. They can be different:
- steel;
- copper;
- propylene;
- metal-plastic.
All of them perform one single function - this is the transportation of coolant from the boiler room (boiler) to the radiators, which, in turn, give off heat and thereby heat the room. All batteries are connected to the system with threads. To do this, fittings with a transition to thread are installed on the circuit. They are placed on polymer contours by soldering or pressing. Copper can only be soldered, while steel can be connected using press fittings and threads.
In any case, a threaded connection is supplied to the battery. How to connect a heating battery to
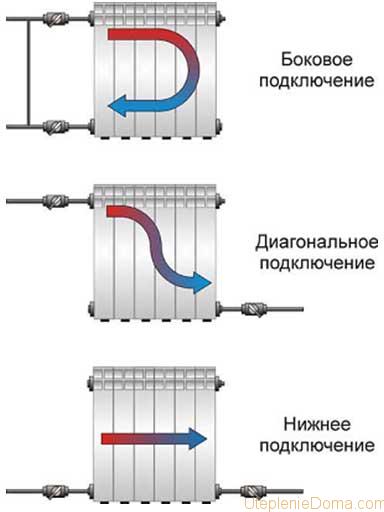
Diagrams for connecting batteries to heating
pipe, diagrams:
- bottom connection;
- side connection;
- diagonal connection.
Most effective option- this is the diagonal. In this case, the supply to the battery is carried out from above, and the return flow comes out from the bottom of the opposite end. Radiator temperature difference at various methods connection is unimportant, so first of all you should start from the location of the battery. New batteries are always supplied with parts for connecting them:
- nuts marked “S” and “O”;
- stub;
- Mayevsky crane.
Before connecting the heating radiator to the pipe, nuts are screwed into the holes at the ends of the battery, and then, depending on the wiring, plugs, a Mayevsky tap and American ones are screwed into them.
To connect the pipes and the circuit, you must use taps and American connections.
An American is a nut that can rotate while the fitting is stationary. By the way, when connecting heating pipes to a heating boiler, it is also necessary to install taps with American type. In this case, it is necessary that the American one is screwed not onto the boiler pipe, but onto the circuit. Then you can safely remove the boiler and water will not spill out of it.
Some craftsmen do not install taps when tying batteries, which leads to difficulties in further operation. If you want to remove and clean the battery, you will have to drain all the water from the system and then refill it. And if something happens in winter and the radiator ruptures, what then? It turns out that you will need to stop the entire heating system to replace it. This is despite the fact that hardly anyone has a spare radiator on duty at home.
You will need to go to the store, buy it, find a master. This will take at least half a day, with sub-zero temperature outdoors there is a risk of the system defrosting. And then it will be necessary not only to change the batteries, but also to repair the entire circuit. If you install taps, you can cut off radiators without stopping the entire system.
Expert approved
A situation with a leaking heating circuit is not uncommon, since the heating system consists of many components and elements, the tightness of their connection with each other is sooner or later broken. In addition to joints, a depressurization zone can also be an entire span of pipe that is physically worn out or damaged due to the influence of some factor.
Sealant for heating pipes produced by different types and execution.
The first thing to do if the seal is broken heating system, this is to eliminate the coolant leak, thoroughly or temporarily - before production overhaul. And the main thing that needs to be ensured when installing heating is its reliable tightness.
The listed factors determine the requirements for sealants used in the installation and repair of water heating systems:
- ease of use;
- heat resistance;
- high adhesion and strength;
- fairly rapid achievement of a sealing effect;
- safety of use.
Types of sealing compounds, their characteristics and methods of application
Based on the place of use, sealants for heating systems are divided into compositions:
- for external use - applied to the site of damage to the pipeline from the outside and, after curing, restores the tightness of the system;
- For internal use(liquid, volumetric action) - introduced into the circuit and seals damage from the inside;
- sealing - applied to gaskets and threads to improve the tightness of connections.
The choice of sealant type depends on the degree of damage and accessibility of the repair site. In addition, the choice of sealing composition determines the method of preparing the heating system for the upcoming repair.
Let's consider sealants in relation to common types of damage and connections of heating system elements.
Sealing compounds for external use
These sealants are produced as one or two component sealants.
Considering that the coolant in the pipes of the heating system is not only hot, but also under pressure, damage to the pipeline should be sealed with particular care. First of all, the sealant must be designed for operation at high temperatures, which is indicated on its packaging in the form of the “heat resistant” marking and the operating temperature range.
Important! Acrylic-based sealant (acrylic) is used only for sealing cold water pipelines. Acrylic glue is not suitable for repairing pipes of heating and hot water systems, since after curing it is not plastic and therefore collapses due to thermal deformations of the base.
Among the one-component compositions for repairing water heating systems, silicone-based sealing adhesives are common.
Heat-resistant silicone-based sealants
To restore the tightness of heating systems from the outside, the most common use of sealants based on various types of silicone, including rubber.
For repair steel pipes it is necessary to use neutral types of silicone (a mark with this parameter is on the package), because those produced are also “acidic” silicone adhesives, which form acetic acid during curing, react with the metal.
If the material meets the required temperature requirements, it is necessary to enhance the effectiveness and reliability of its application with additional means to ensure success. As a rule, the manufacturer recommends such sealants for use as a filler for cracks or holes. If the material indicates another application, but its characteristics and potential are high, the adhesive is quite suitable for use. For example, a composition recommended for sealing components on an engine can easily cope with the same task in a home heating system.

And yet, taking into account the responsibility of application, applying silicone sealants on heating system pipes it is necessary in combination with a reinforcing mesh, for which strip fiberglass tape “serpyanka” is successfully used.
![]()
Sealing method
A layer of sealant is applied to the prepared surface of the pipe (drying, cleaning, degreasing), on top of which coils of serpyanka are laid end-to-end, then sealant again, after which the tape is wound in turns with an overlap of 1 cm. The number of layers of serpyanka with glue between them should be 4-5 , it is necessary to prevent the formation of air bubbles or loose areas between them. The last 2-3 turns of the serpyanka are made on a section of the pipe without glue and are tightly attached to it with a nylon clamp, which, after the silicone has cured, will be removed along with the excess turns of the tape. The top repair layer is made of sealant and smoothed out.
Work should be carried out at a temperature not lower than +5 °C, silicone should be at room temperature (20-25 degrees). Curing of the composition, which occurs due to contact of silicone with moisture, occurs depending on the type of silicone and amounts to several millimeters per day.

Two-component compositions for repairing heating and hot water systems are different kinds based adhesives epoxy resins and polyurethane.
These compositions are less common for pipeline repairs, since they require certain skills in maintaining proportions when preparing the mixture, have a short “survival” time of the solution after mixing the components, and have a high cost relative to other adhesives.

There are also one-component polyurethane sealants that cure upon contact with air. The quality of these mixtures is also high, curing takes a little longer than two-component compositions, and they are also much more expensive in price than silicone materials. The main disadvantage of polyurethane sealants is toxicity during operation - the room must be good ventilation, and work should be carried out in protective clothing and gloves to avoid contact of glue on exposed skin.

To guarantee success when using two-component compositions, it is also necessary to carefully prepare the section of pipe being repaired and use reinforcing tape – serpyanka – in combination with glue.
Liquid sealants
Such sealants are used in situations where, in order to detect a leak, a large amount of dismantling of the decorative and insulating shells of the heating system (for example, a “warm floor” system) must be done, or the intensity of the leak is insignificant - no coolant leak is observed, but its volume decreases, and the pressure in the system is reduced when the circulator pump is running.
Important! If there is visually no leakage point and low pressure in the heating system, before adding liquid sealant to the circuit, it is necessary to check the functionality expansion tank– a drop in coolant pressure can also be caused by the destruction of its membrane.
Liquid sealant, unlike adhesives for external use, affects damage to the pipeline or radiator from the inside. The sealing compound is introduced into the coolant of the circuit cut off from the main heating system. When the sealant is added to water, no reaction occurs, but in places of leakage where the coolant comes into contact with air, polymerization of the glue begins and sealing of the damage.
Many types of liquid sealants are produced, focused on use in certain heating systems, differing in the type of coolant, fuel of the heating unit, material of the pipeline, radiators, etc.

If the leakage of the system is not significant, and the sealing compound is selected and used correctly, then the likelihood of success in eliminating the damage from the inside is high.
Important! In heating systems with pipes and radiators made of steel or aluminum, if sealing is necessary, it is permissible to use a means to repair the car’s cooling system, but not the powder type, which settles in the lower part of the pipeline and its elements, but the liquid one.

Mode of application
This means of combating leaks in heating systems is relatively new, and universal technology there is no use for it, although the principle of action is common for all liquid formulations.
The sealant is purchased in accordance with the characteristics of the heating system installed in the home. In addition, when buying a composition, you need to know how much coolant it holds heating circuit in order to purchase the sealant in the required quantity - the glue instructions indicate the concentration in which it should be present in the system.
The use of each type of such sealant has its own nuances: the permissibility of the presence of filters in the circuit, the method of introducing the composition into the coolant, the duration of action, the size of the damage, the possibility of the presence of glue in the system after achieving the effect, etc. Algorithm for performing sealing liquid composition is described in detail in the instructions for its use, but often to perform this operation independently it is necessary to have special tool or equipment, such as a compact electric pump for the initial introduction of sealant into the circuit and its complete dissolution and uniform distribution throughout the entire volume of the coolant. Therefore, without practical skills in this matter, it is better to contact specialists who will perform this procedure without possible negative consequences such as system clogging or failure of its components.
Sealing sealants
To ensure the sealing of threaded connections, many years ago flax tow was used, strands of which were wound on external thread and covered with red lead on natural drying oil(GOST), after which the joint was assembled along the thread. With the advent of modern artificial coolants in heating systems, tow partially lost its effectiveness due to the high degree of permeability of antifreeze and gave way to FUM tape, although it is used in combination with a special Unipak paste, which also contains flax fibers, when assembling cast iron pipelines of large diameters or simply due to the lack of fluoroplastic.

FUM tape is a synthetic fluoroplastic material of a matte, less often transparent color, which, due to its fluorine content, can withstand mechanical and temperature impacts without compromising its qualities.
Depending on the conditions of use, fluoroplastic tape is produced in several varieties:
- industrial, containing 20% petroleum jelly;
- household;
- for acidic environments;
- for systems with special requirements for environmental cleanliness.
Important! Fum tape is used for sealing connections in systems with cold and hot water at a maximum pressure value of 9.5 MPa.
Rules of application:
- the tape is wound tightly, with slight tension, in the direction of the thread;
- the end of the tape should not be located at the end of the joint.
FUM tape is wound onto the thread in a number of layers depending on the diameter of the thread:
- Ø 16-25 mm – 3 layers;
- Ø 25-42 mm – 4 layers.
The number of layers is very arbitrary, since low-quality material will require twice as much consumption.

Disadvantages of FUM tape:
- when assembling rough threaded connections, the tape breaks and is squeezed out;
- does not have adhesion to the surface of materials;
- does not provide sealing of threads with a diameter of more than 25 mm, therefore cannot be used when assembling heating radiators.
To seal threaded connections, liquid and paste-like compounds are also used, which can dry out or remain elastic throughout their service life.
An example is the same non-hardening paste “Unipak” with flax fibers in the composition, used as independent material, ensuring not only the tightness of threaded connections, but also their protection against corrosion, as well as ease of disassembly
Drying pastes are solvent-based sealants, modern material, plastic when assembling the joint and hardening after a certain time. For more effective use can be used in combination with flax strands, which slow down the assembly process; after drying, they provide a strong connection without shrinkage during operation.
The disadvantage is the impossibility of tightening the threaded connection without breaking the tightness of the joint.
Anaerobic sealants are ready-to-use mixtures that differ in properties depending on the conditions of use (pressure, temperature, vibration), thread diameter, assembly density, etc.
Advantages:
- ease of use;
- low labor intensity of the process due to lubricating properties;
- seals the threaded connection even with low assembly force;
- wide range of operating pressures of the medium in the pipeline;
- easy removal of excess mixture upon completion of work;
- presence of species with to varying degrees fixation;
- optimal price-quality ratio.
Anaerobic sealants are applied to both threaded surfaces being connected (internal and external), previously cleaned and degreased. The instructions for use, as a rule, indicate the air temperature permissible for the work - usually it is about 15 degrees Celsius (if no curing accelerators are used in the process).

An example of an anaerobic glue is the universal heat-resistant sealant for heating pipes PERMATEX 59214, which has proven itself well on the Russian market.
Sealing and sealing fixation compound medium strength, heat-resistant and vibration-resistant, allows adjustment of the threaded connection within 24 hours after completion of assembly. Maximum operating pressure– 700 atm., maximum temperature + 200°C.
Conclusion
Sealant for repairing and connecting heating pipes is a material that is impossible to do without when installing a heating system, so the importance of choosing this material when installing and repairing coolant circuits is difficult to overestimate. From which it follows that when purchasing adhesives you need to give preference to products famous manufacturers, whose rating on the Russian market is quite high.