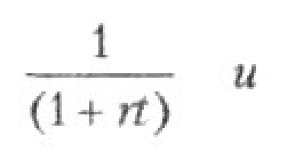What is an ordered series? Statistics. Basic concepts and definitions (2019). Volume and Scope
Statistics is an exact science that studies methods of collecting, analyzing and processing data that describe mass actions, phenomena and processes. Mathematical statistics is a branch of mathematics that studies methods of collecting, systematizing and processing the results of observations of random mass phenomena in order to identify existing patterns.

Statistics studies: the number of individual groups of the population of the country and its regions, the production and consumption of various types of products, the transportation of goods and passengers by various modes of transport, natural resources and much more. The results of statistical studies are widely used for practical and scientific conclusions. Currently, statistics begins to be studied in secondary school; in universities it is a compulsory subject, because it is associated with many sciences and fields. To increase the number of sales in a store, to improve the quality of knowledge in school, to move the country towards economic growth, it is necessary to conduct statistical studies and draw appropriate conclusions. And everyone should be able to do this.

Formation of skills in primary processing of statistical data; image and analysis of quantitative information presented in different forms (in the form of tables, diagrams, graphs of real dependencies); developing ideas about important statistical ideas, namely: the idea of estimation and the idea of testing statistical hypotheses; developing the ability to compare the probabilities of random events occurring with the results of specific experiments. The main goals of studying the elements of statistics

Contents Data series Volume of data series Range of data series Mode of data series Median of series Arithmetic mean Ordered data seriesOrdered data series Data distribution table Data distribution table Let's summarize Nominative data series Frequency of result Percentage frequency Data grouping Methods of data processing Let's summarize






Definition The mode of a data series is the number in the series that appears most frequently in that series. A data series may or may not have a mode. Thus, in the data series 47, 46, 50, 52, 47, 52, 49, 45, 43, 53, each of the numbers 47 and 52 occurs twice, and the remaining numbers less than twice. In such cases, it was agreed that the series has two modes: 47 and 52.

Complete the task: So, in the data series 47, 46, 50, 52, 47, 52, 49, 45, 43, 53, each of the numbers 47 and 52 appears twice, and the remaining numbers appear less than twice. In such cases, it was agreed that the series has two modes: 47 and 52. At the institute they took a test in higher mathematics. There were 10 people in the group, and they received the corresponding ratings: 3, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 5. Determine the mode of this series. Answer: 4

Definition: A median with an odd number of terms is the number written in the middle. A median with an even number of terms is the arithmetic mean of the two numbers written in the middle. For example: determine the median of a series of numbers 1) 6; -4; 5; -2; -3; 3; 3; -2; 3. Answer: -3 2) -1; 0; 2; 1; -1; 0;2; -1. Answer: 0


Definition The arithmetic mean is the quotient of dividing the sum of the numbers in a series by their number. For example: given a series of numbers -1; 0; 2; 1; -1; 0; 2; -1. Then the arithmetic mean will be equal to: ((-1)+0+2+(-1)):8 =2:8=0.25


PRACTICAL WORK Assignment: characterize the performance of student Ivanov in mathematics for the fourth quarter. PERFORMANCE OF THE WORK: 1.Collection of information: Grades written out from the magazine: 5,4,5,3,3,5,4,4,4. 2. Processing of the received data: volume = 9 range = = 2 mode = 4 median = 3 arithmetic mean =(): 9 4 Characteristics of academic performance: the student is not always ready for the lesson. Mostly he studies with grades "4". A quarter comes out to “4”.

Independently: You need to find the volume of the series, the range of the series, mode, median and arithmetic mean: Card 1. 22.5; 23; 21.5; 22; 23. Card 2. 6; -4; 5; -2; -3; 3; 3; -2; 3. Card 3. 12.5; 12; 12; 12.5; 13; 12.5; 13. Card 4. -1; 0; 2; 1; -1; 0; 2; -1. Card; 130; 124; 131. Card; 100; 110.

Let's check Card 1. volume of series = 5 range of series = 10 mode = 23 median = 21.5 arithmetic mean = 13.3 Card 3. volume of series = 7 range of series = 1 mode = 12.5 median = 12.5 arithmetic mean = 12.5 Card 2. volume of series = 9 range of series = 10 mode = 3 median = -3 arithmetic mean = 1 Card 4. volume of series = 8 range of series = 3 mode = -1 median = 0 arithmetic mean = 0.25


Definition Ordered series of data are series in which the data is arranged according to some rule. How to order a series of numbers? (Write the numbers so that each subsequent number is no less (no more) than the previous one); or write down some names “alphabetically”...

Complete the task: Given a series of numbers: -1;-3;-3;-2;3;3;2;0;3;3;-3;-3;1;1;-3;-1 Arrange it in ascending order numbers. Solution: -3;-3;-3;-3;-3;-2;-1;-1;0;1;1;2;3;3;3;3 The result is an ordered series. The data itself has not changed, only the order in which they appear has changed.

Definition A data distribution table is a table of an ordered series in which, instead of repeating the same number, the number of repetitions is recorded. Conversely, if the distribution table is known, then an ordered series of data can be compiled. For example: From it the following ordered series is obtained: -3;-3;-3;-1;-1;-1;-1;5;5;7;8;8;8;8;8 Measurement result - 3578 How many times occurs in the data series 34215

Complete the task: In a women's shoe store, statistical research was carried out and a corresponding table was compiled for the price of shoes and the number of sales: Price (rubles): Quantity: For these indicators, you need to find statistical characteristics: create an ordered series of data volume of the data series range of the series mode of the series median of the series arithmetic mean of a data series


Let's summarize: We got acquainted with the initial concepts of how statistical data processing occurs: 1) data is always the result of some kind of measurement 2) for a series of some data you can find: volume, range, mode, median and arithmetic mean 3) any series of data you can organize and create a table of data distribution

Definition A nominative series of data is NOT NUMERICAL DATA, but, for example, names; titles; nominations... For example: list of finalists of the World Cup since 1930: Argentina, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Brazil, Hungary, Sweden, Czechoslovakia, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Netherlands, Germany, Germany, Argentina, Italy, Brazil, Germany, France


Definition The probability of a random event is equal to a fraction, the denominator of which contains the number of all equally probable possibilities that make up a certain event, and the numerator - the number of those possibilities in which the event in question occurs. For example:



 34 Schedule:
34 Schedule:


Text HTML version of the publication
Algebra lesson notes in 7th grade
Lesson topic: “MEDIAN OF AN ORDERED SERIES.”
teacher of the Ozyornaya school, branch of the MCOU Burkovskaya secondary school Eremenko Tatyana Alekseevna
Goals:
the concept of median as a statistical characteristic of an ordered series; develop the ability to find the median for ordered series with an even and odd number of terms; to develop the ability to interpret the values of the median depending on the practical situation, to consolidate the concept of the arithmetic mean of a set of numbers. Develop independent work skills. Develop an interest in mathematics.
During the classes
Oral work.
The rows are given: 1) 4; 1; 8; 5; 1; 2) ; 9; 3; 0.5; ; 3) 6; 0.2; ; 4; 6; 7.3; 6. Find: a) the largest and smallest values of each series; b) the scope of each row; c) the mode of each row.
II. Explanation of new material.
Work according to the textbook. 1. Let's consider the problem from paragraph 10 of the textbook. What does ordered series mean? I would like to emphasize that before finding the median, you must always order the data series. 2.On the board we get acquainted with the rules for finding the median for series with an even and odd number of terms:
Median
orderly
row
numbers
With
odd
number
members
is the number written in the middle, and
median
ordered series
numbers
with an even number of members
is called the arithmetic mean of two numbers written in the middle.
Median
arbitrary
row
called median 1 3 1 7 5 4
I note that the indicators are the arithmetic mean, mode and median according to
differently
characterize
data,
received
result
observations.
III. Formation of skills and abilities.
1st group. Exercises on applying formulas for finding the median of an ordered and unordered series. 1.
№ 186.
Solution: a) Number of members of the series P= 9; median Meh= 41; b) P= 7, the row is ordered, Meh= 207; V) P= 6, the row is ordered, Meh= = 21; G) P= 8, the row is ordered, Meh= = 2.9. Answer: a) 41; b) 207; at 21; d) 2.9. Students comment on how to find the median. 2. Find the arithmetic mean and median of a series of numbers: a) 27, 29, 23, 31, 21, 34; V) ; 1. b) 56, 58, 64, 66, 62, 74. Solution: To find the median, it is necessary to order each row: a) 21, 23, 27, 29, 31, 34. P = 6; X =
= 27,5;
Meh =
= 28;
20
22
2
+
2, 6
3, 2
2
+
1125
;
;
;
3636
21
23
27
29
31
34
165
66
+++++
=
27
29
2
+
№ 188
(orally). Answer: yes; b) no; c) no; d) yes. 4. Knowing that an ordered series contains T numbers, where T– an odd number, indicate the number of the member that is the median if T equals: a) 5; b) 17; c) 47; d) 201. Answer: a) 3; b) 9; c) 24; d) 101. 2nd group. Practical tasks on finding the median of the corresponding series and interpreting the result obtained. 1.
№ 189.
Solution: Number of series members P= 12. To find the median, the series must be ordered: 136, 149, 156, 158, 168, 174, 178, 179, 185, 185, 185, 194. Median of the series Meh= = 176. Monthly output was greater than the median for the following members of the artel: 56 58 62 64 66 74 380 66 +++++ =≈ 62 64 2 + 1125 ; ; ; 3636 1125 12456 18 1:5:5 6336 6 6 ++++ ⎛⎞ ++++ = = ⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ 2 3 67 174 178 22 xx + + = 1) Kvitko; 4) Bobkov; 2) Baranov; 5) Rilov; 3) Antonov; 6) Astafiev. Answer: 176. 2.
№ 192.
Solution: Let's sort the data series: 30, 31, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 33, 35, 35, 36, 36, 36, 38, 38, 38, 40, 40, 42; number of series members P= 20. Swing A = x max – x min = 42 – 30 = 12. Fashion Mo= 32 (this value occurs 6 times - more often than others). Median Meh= = 35. In this case, the range shows the greatest variation in the time for processing the part; the mode shows the most typical processing time value; median – processing time, which was not exceeded by half of the turners. Answer: 12; 32; 35.
IV. Lesson summary.
– What is the median of a series of numbers called? – Can the median of a series of numbers not coincide with any of the numbers in the series? – What number is the median of an ordered series containing 2 P numbers? 2 P– 1 numbers? – How to find the median of an unordered series?
Homework:
№ 187, № 190, № 191, № 254. 10 11 35 35 22 xx + + =
municipal budgetary educational institution of Mtsensk
Topic: “Series of quantities.”
Goal: to introduce children to increasing and decreasing series.
During the classes.
1. Introduction of the concept of “ordered series”.
On the demonstration table there are two sets of identical vessels with different volumes. Children have 4 stripes of different lengths and different colors. One set of vessels is arranged in order of decreasing volumes. The volumes of the second set of vessels are arranged without order.
I have two sets of vessels. Tatyana Vasilyevna put it like this (point to a set of vessels, arranged in no order), and I did so (point to a set of vessels, arranged in order of decreasing their volumes). Compare these sets. Are they the same or different? Identical, on what grounds? Different, on what grounds? How did you install it?
(Children find out that one set was built in order. The second set of volumes, built without order, is removed).
Today we will work with such a row (point to the remaining row), it is called ordered. On what basis were the vessels ordered? Show this row using the lengths of the stripes.
(Children work independently. The teacher walks around the class and looks at what the children have laid out. These options are put on the board).
Possible options:
The teacher points to option 3. Children evaluate with “+” or “-” signs. Find out why you disagree. Where is the mistake? It turns out that the strips are laid out out of order. Return to the vessels. Remove strips from the board. The second option is dealt with similarly. It turns out that the strips are laid out in a different order. Remove this option from the board. Children evaluate the first option. It turns out that he is faithful.
Lay it out like mine. Indicate the volumes of water with letters on the strips. The largest volume is A. (Children mark it on their stripes, the teacher – on their stripes). The next strip less than A will be designated P. The next strip less than P will be denoted by the letter N. The smallest strip will be denoted by the letter K.
(The result is a row: A, P, N, K).
Let's play the game "Guess the volume." Name the largest volume, the smallest. What volume is less than K? More A? What volume is greater than P? Less P? What is the intended volume if it is greater than K but less than P? More K, but less A?
Fizminutka
2. Introduction of terms: quantities are arranged in ascending and descending order.
Textbook, part 2 p. 11. Ex. 2.
In the textbook and on the board:
We have strips with area H and area B. Draw strips with area P and B to make an orderly row.
(Children work independently. The teacher puts three options for completing the task on the board).
https://pandia.ru/text/78/408/images/image011_20.gif" width="21" height="74">
N B R V N B R V N B R V
I did this task at home and got the following drawings. (Show first picture). Did I draw it right or wrong? What mistake did I make? How should you draw it? Will this series be ordered? Is there anyone in the class who did this? We made the same mistake, next time we will be more careful.
(The first picture is removed. Show the second picture. Disassemble the second picture in the same way).
Look at the third picture. Did I draw it right or wrong? Why?
(It turns out that the third picture is correct).
If anyone got it wrong, erase it and draw it like I did. Find the entry below. You need to compare areas B and C (one child is at the board). Find area B and C. What can you say about these areas? Let's write down area B is less than area C. We write and say: “Area B is less than area C.”
(Areas P and H are compared in the same way).
We have built the values from smallest to largest. This means that the values are arranged in an ascending series. (Attach a sign “in ascending order” above the areas H, B, R, V, read).
Fizminutka
In the textbook:
We have segments L and S. They indicate the length. Draw segments T and E so that you get an ordered series.
(Children work independently. The teacher walks around the class and puts the resulting rows on the board).
Possible options.
Anxiety is a child of evolution
Anxiety is a feeling familiar to absolutely every person. Anxiety is based on the instinct of self-preservation, which we inherited from our distant ancestors and which manifests itself in the form of a defensive reaction “Flight or fight.” In other words, anxiety does not arise out of nowhere, but has an evolutionary basis. If at a time when a person was constantly in danger in the form of an attack by a saber-toothed tiger or an invasion of a hostile tribe, anxiety really helped to survive, then today we live in the safest time in the history of mankind. But our instincts continue to operate at a prehistoric level, creating many problems. Therefore, it is important to understand that anxiety is not your personal flaw, but a mechanism developed by evolution that is no longer relevant in modern conditions. Anxious impulses, once necessary for survival, have now lost their expediency, turning into neurotic manifestations that significantly limit the lives of anxious people.
Distribution range is a sequence of numbers indicating the qualitative or quantitative value of a characteristic and the frequency of its occurrence.
Types of distribution series are classified according to different principles.
According to the degree of ordering, the rows are divided into:
disordered
ordered
Unordered row- this is a series in which the values of a characteristic are written in the order in which the options arrived during the study.
Example: When studying the height of a group of students, its values were recorded in cm (175,170,168,173,179).
Ordered series- this is a series obtained from an unordered one in which the values of the characteristic are rewritten in ascending or descending order. An ordered series is called ranked, and the ranking procedure
(ordering) is called sorting.
Example: (Height 168,170,173,175,179)
According to the type of characteristic, the distribution series are divided into:
attributive
variational.
Attributive series- this is a series compiled on the basis of a qualitative characteristic.
Variation series- this is a series compiled on the basis of a quantitative characteristic.
Variation series are divided into discrete, continuous and interval.
Variational discrete, continuous and interval series are named according to the corresponding feature that underlies the compilation of the series. For example, a series by shoe size is discrete by body weight - continuous.
Methods of representing series in practical and scientific medicine are divided into three groups:
Tabular presentation;
Analytical representation (in the form of a formula);
Graphic representation.
1. The simplest table consists of two columns or two rows, one of which contains the values of the characteristic x i in an ordered form, and in the other - the relative or absolute frequency of its occurrence n i , f i .
Example: Tabular presentation of grades in a group x i and the number of students who received them n i .
|
x i | ||||
|
n i |
2. Graphical representation of series is based on tabular data. Graphs are constructed in a rectangular coordinate system, where attribute values are always plotted horizontally X i , and vertically the absolute or relative frequency n i .
Basic ways of presenting graphs:
Diagram in segments.
bar chart
Frequency polygon.
Variation (frequency) curve.
Bar chart is a graph representing a series in the form of vertical straight line segments, the position of which on the horizontal is determined by the value of the attribute, and the length of the segment is proportional to its absolute or relative frequency.
Example: bar chart for group performance assessments.
n i
5 4 3 2 XI
Typically, segment diagrams are constructed for discretely specified characteristics with a small number of options.
bar chart- this is a graph in the form of a stepped figure of rectangles adjacent to each other, the bases of which are intervals of feature values, and the heights of the rectangles are proportional to frequency or frequency (the number of objects falling within the interval). The areas of the rectangles correspond to the number of groups in a given interval.
Histograms are graphs of interval series. They are built primarily for large volumes of aggregates.
Example: Histogram of the normal distribution of red blood cells in human blood. Horizontal - cell diameter X i (mk), vertically - frequency n i number of cells in the interval.
n
 i
i
2 4 6 8 10 12 x i
Poligon (polygon) of frequencies- a series graph represented by a broken line of a point - the vertices of which correspond to the midpoints of the intervals, and the height of the point above the horizontal is proportional to the frequency or frequency.
Polygons are constructed for continuous and discrete variation series in cases where the average values of a characteristic are identified in the intervals. Polygons are preferable to histograms for continuous distribution series
Example: a frequency polygon based on a histogram of the distribution of red blood cells in human blood.
n
 i
i
2 4 6 8 10 12 x i
Variation (frequency) curve- a graph of a series obtained under the condition that the volume of the population tends to infinity ( N→∞) , and the length of the interval itself tends to zero (Δ X→0) .
For practical statistical calculations, four groups of frequency distributions have been identified as standards:
Rectangular distribution.
Bell-shaped unimodal (single-vertex) distribution.
Bimodal (two-vertex) distribution.
Exponential distribution:
growing,
decreasing.

n i
x i
x i
x i
x i
Random equally probable events are subject to a rectangular distribution.
A wide class of phenomena (indicators of mental and physical development, height, weight, etc.) is subject to a bell-shaped symmetrical distribution. In practice, the most common unimodal distribution is the symmetrical one, which is why its classical form is called the normal distribution.
The bimodal distribution corresponds, for example, to the performance of students with and without a long break in their studies.
An exponentially decreasing distribution corresponds to the distribution of income in a capitalist society (the frequency decreases as income increases).