Heat storage for heating. A heat accumulator is an important element of the heating system for a comfortable and safe home. Functions of heat accumulators
During the heating of the house, it often happens that during the daytime it is possible to generate excess heat, and at night it is not enough. There is also the opposite situation, in which it is more profitable to use heating at night. Such moments will help smooth out the heat accumulator for heating. But you need to know how to choose it correctly, install it and connect it to the system. You can find detailed information on this topic from this article.
When you need a heat accumulator
This simple element of the heating system in the form of an insulated water tank is recommended to be installed in such cases:
- for the most efficient operation of a solid fuel boiler;
- together with an electric heat generator operating at a reduced night rate.
For reference. There are also water heat accumulators for greenhouses, used to store solar energy received during the day.
The operation of solid fuel boilers has its own characteristics. The heat generator operates with high efficiency only when operating at maximum modes, if you shut off the air to lower the temperature in the furnace, then the efficiency also decreases. The homeowner also has a lot of worries about the frequency of burning, the firewood has burned out - it is necessary to load new ones, it is extremely inconvenient to do this in the middle of the night. The solution is simple: you need a storage tank that accumulates the heat generated earlier to use it after the firewood burns out in the firebox.

The opposite situation occurs with an electric boiler connected to the network through a multi-tariff meter. To save money, you need to get maximum heat at night, when the tariff is low, and do not use electricity during the day. And here the heat accumulator in the heating system will allow you to organize the optimal schedule for the operation of the heat source, giving out hot water to the system while the heat generator is idle.
Important. To work together with a heat accumulator, the boiler must have at least one and a half reserve in terms of thermal power. Otherwise, he will not be able to simultaneously heat the water in the heating system and the storage tank.

A similar situation with excess heat occurs in greenhouses, in the daytime they are even ventilated. In order to accumulate solar energy for use at night, you can use the simplest heat accumulator of Lezhebok to heat the ground. This is a black polymer sleeve filled with water and laid directly on the bed, it does not allow the soil to cool down at night. To absorb more heat, barrels of water, painted black, are placed inside the greenhouse.

Heat accumulator calculation
A container for the accumulation of thermal energy can be either purchased ready-made or made independently. But a natural question arises: what capacity should the tank be? After all, a small tank will not give the desired effect, and too much will cost a pretty penny. The answer to this question will help to find the calculation of the heat accumulator, but first you need to determine the initial parameters for the calculations:
- heat loss of the house or its quadrature;
- duration of inactivity of the main heat source.
Let us determine the capacity of the storage tank using the example of a standard house with an area of 100 m2, which requires an amount of heat in the amount of 10 kW to heat. Assume that the net downtime of the boiler is 6 hours, the average temperature of the heat carrier in the system is 60 °C. Logically, during the period of time while the heating unit is idle, the battery must supply 10 kW to the system every hour, for a total of 10 x 6 = 60 kW. This is the amount of energy that should be accumulated.

Since the temperature in the tank should be as high as possible, for calculations we will take a value of 90 ° C, domestic boilers are still unable to do more. The required capacity of the heat accumulator, expressed in mass of water, is calculated as follows:
- m = Q / 0.0012 Δt
In this formula:
- Q is the amount of accumulated thermal energy, in our case it is 60 kW;
- 0.0012 kW / kg ºС is the specific heat capacity of water, in more familiar units of measurement - 4.187 kJ / kg ºС;
- Δt is the difference between the maximum temperature of the coolant in the tank and the heating system, ºС.

So, the water accumulator should contain 60 / 0.0012 (90 - 60) = 1667 kg of water, which is approximately 1.7 m3 in volume. But there is one point: the calculation is made at the lowest temperature outside, which happens infrequently, excluding the northern regions. In addition, after 6 hours, the water in the tank will only cool down to 60 ºС, which means that in the absence of cold weather, the battery can be “discharged” further until the temperature drops to 40 ºС. Hence the conclusion: for a house with an area of 100 m2, a storage tank with a volume of 1.5 m3 is enough if the boiler is inactive for 6 hours.
It follows from the previous section that it will not be possible to get rid of an ordinary 200-liter barrel, unless its capacity is at least half a cube. This is enough for a house of 30 m2, and then not for long. In order not to waste time and energy in vain, it is necessary to 
From the point of view of placement in the boiler room, it is better to make a rectangular container. Dimensions are arbitrary, the main thing is that their product is equal to the calculated volume. The ideal option is a stainless steel tank, but ordinary metal will do.

At the top and bottom, a do-it-yourself heat accumulator must be provided with nozzles for connecting to the system. So that the steel walls do not bulge outward with water pressure, the structure must be tightened with ribs or jumpers.

The battery tank must be well insulated, including from below. For this purpose, foam plastic with a density of 15-25 kg / m3 or mineral wool in slabs of at least 105 kg / m3 density is suitable. The optimal thickness of the heat-insulating layer is 100 mm. The resulting apparatus, filled with coolant, will have a decent weight, so a foundation will be required for its installation.

Advice. If you need a container for a gravity heating system, then you should install it yourself on a metal stand, not forgetting to insulate the lower part. The goal is to raise the tank above the level of the batteries.
Wiring diagram
After the tank is in place, it must be properly connected to the piping network. The most popular is the standard heat accumulator connection diagram shown in the figure:

To implement it, you will need 2 circulation pumps and the same number of three-way valves. Pumps provide circulation in separate circuits, and valves provide the required temperature. In the boiler circuit, it should not fall below 55 ºС in order to avoid the appearance of condensate in the solid fuel boiler, this is what the valve on the left side of the diagram does.
The heat carrier in the heating pipelines is heated depending on the heat demand, and therefore the connection of the heat accumulator on the other side is also carried out through the mixing unit. The valve can control the water temperature in automatic mode, focusing on the sensor or using a thermostat. One of the schemes of a heating system with a heat accumulator (buffer tank) is shown in the video.
Conclusion
A heat storage tank can make life easier for owners of solid fuel boilers. They don't have to worry about loading fuel at night, which is a big plus. And the heat generator itself will begin to work in an economical mode, developing the highest efficiency. As for electric boilers, then the benefit when installing the drive is obvious.
In most modern heating systems, there is an inherent defect that makes it impossible to effectively organize heating using a periodic heating boiler. The problem lies not in the principle of fuel combustion, although not everything is going smoothly there either, but in the organization of heat transfer from a heat source - a solid fuel combustion front into the air space of living rooms of a house or apartment. Heat accumulators are designed to compensate for losses caused by the periodic operation of the boiler. To be precise, a heat accumulator is necessary for any periodic heating boiler.
The device, proudly called a heat accumulator for heating boilers, is a tank of considerable capacity, in some cases reaching up to 10 tons of water, with a system of internal heat exchangers. What should the use of a heat accumulator give:
- Safe accumulation of excess heat generated by the boiler in the water flow of the coolant;
- To increase the duration of the heating-cooling cycle of the boiler plant, thereby simplifying its maintenance, freeing it from the need to start it at night or at an inconvenient time for oneself;
- To increase the efficiency of work and increase the resource of heating boilers.
Interesting ! The primitive design of the heat accumulator for heating boilers allows you to make it yourself, you only need a water tank, pipes for connection, valve equipment and a welding machine.
In addition to a solid fuel heating boiler, there is also a need to use a heat accumulator for systems based on electric heating boilers. In this case, the use of a heat accumulator is dictated by an artificial choice in favor of periodic heating, and only at night, when it is possible to use a more favorable preferential tariff.

The design of modern heating boilers for the sake of the manufacturer is maximally optimized in terms of costs and production costs. A modern heating boiler is made of thin sheet steel with minimal costs for scarce and expensive copper and nickel, and operates in the “potbelly stove” mode.
In his device there is not even a hint of a heat accumulator. Such a heating boiler, in principle, is not capable of accumulating thermal energy. Compare a modern pellet or coal boiler with the old, heavy cast iron boilers, or even better, with the device of an ordinary rustic stone stove. In the latter case, the functions of a heat accumulator are most effectively performed by brickwork, which directly absorbs heat from the flame and evenly transfers it into the air of the room for 10-12 hours.
Therefore, a modern heating boiler is inefficient without a heat accumulator. A solid fuel unit will be indispensable in operation and will do without multi-ton heat accumulators if its device has a system for automatically loading fuel into the furnace and subsequent ash removal.
How does a heat accumulator work
The purpose of the heat accumulator is to provide additional thermal energy to the water heating circuit after the reduction or cessation of heat generation by the heating boiler. To do this, in a huge container there is a large amount of boiling water at a pressure of about 3 atm. A heat exchanger is soldered into the tank body, through which heat is “pumped” into the accumulator and re-extracted into the heating system. Often an additional heat exchanger is built into the tank in order to obtain hot water for the needs of the kitchen and bathroom.
The principle of mixing flows of different temperatures
To quickly heat up the room, the heat accumulator is disconnected from the circuit of the heated coolant with the help of a three-way valve. Only after heating the water flow in the pipes above 60 ° C, water is connected to the circuit from the store of the heat accumulator. And while the boiler is running, the heat goes in two directions: into the storage tank and into the heating radiators.

There are certain benefits to this approach:
- Rapid heating of the living space, and only after that, the excess heat is discharged into the heat accumulator;
- The mixing principle gives an efficient heat exchange;
- The water reserve in the heat accumulator is a strategic reserve for the boiler, thereby preventing its possible burnout in case of violation of water circulation in the heating plant.
Important ! In such a scheme, any non-ferrous metals that give an electrochemical pair with steel and aluminum should be excluded.
Ideally, the water circulating in the hot heat exchanger of the heating boiler should not mix with the heat carrier flowing throughout the heating system. Therefore, a different scheme is often used in heat accumulators - with hydraulic decoupling and flow separation.
System with hydraulic decoupling of thermal carriers
In this scheme, the heat accumulator plays the role of one of the elements of the heat supply circuit; it cannot be excluded from the flow. In fact, in the heat accumulator there is a constant transfer of heat from the allocated "hot" circuit of the heating boiler and the rest of the mass of water or heat carrier circulating in the heating system.
What does it give:
- The highly loaded heat exchanger of the heating boiler requires the use of special water purified from impurities and oxygen from the air. Only such water guarantees a long service life of the heat exchanger tubes and seals. The supply of the required amount of prepared water is stored in an additional boiler.
- By means of a special scheme of heated water from the heat accumulator tank, the temperature of the selected liquid can be easily controlled, which simplifies the heating control system.
The disadvantages include the need for additional devices - two pumps: coolant circulation and power supply systems. Sometimes a pair of devices is used for backup - a voltage converter and an electric battery for a heating boiler. Otherwise, a power outage can lead to a serious accident in the primary circuit.
A more complex and improved scheme involves the use of two independent heat exchangers combined in one heat accumulator housing. This is a more rational way of organizing the operation of a heat accumulator with a high degree of redundancy. It is he who can be recommended for those who want to make a heat accumulator for a heating boiler with their own hands.

Building a heat accumulator on your own
For the manufacture of a heat storage device, it is necessary to determine the thermal power of the battery. There is a certain methodology for building an accumulating system. The amount of water in the accumulator is taken on the basis of 30-40 liters of liquid for every 1000 W of boiler heat output. In this case, for a house of 100m 2 of heated area, a capacity of 350-400 liters will be required. The best option would be to use a ready-made boiler tank, with water level, pressure and temperature sensors.
If an admixing system is selected as a working scheme, which works properly even in the absence of special pumps, a three-position block valve will have to be additionally installed in the heating circuit.

Simpler schemes will require one or two heat exchangers to be installed in the tank
Important ! On the Web, it is often recommended to install copper heat exchangers from a twisted copper pipe 15-17m long and 15-20mm in diameter “through the light”. The recommendation has dubious prospects, since copper and iron corrode intensively in contact with hot water.

It is better to use a heat exchanger made of the same material as the container. This guarantees the normal quality of the weld when installing the heat exchanger. In addition, in the cavity of the heat accumulator it is better to use anode protection with magnesium electrodes, similar to electric hot water boilers. The outer walls of the tank - heat accumulator are sheathed with heat-insulating mats or mineral wool.
Promising options for heat accumulators
One of the interesting solutions was small-sized batteries that use fusible paraffins or silicone oils instead of water. Due to the significantly higher heat capacity, it became possible to use safe small-sized storage systems for electric boilers in apartment heating systems. Instead of a 300-liter heavy capacity, it is planned to use a two-section accumulator with a total volume of 50 liters of coolant, which has a thermal reserve of 15 kW / h.
Note ! Most often, heat accumulators are used as a backup source of heat when growing vegetables in greenhouses, to quickly heat the room during a sharp cold snap or frost.
When using a gas boiler, we do not need to independently maintain a certain temperature in the heating circuit - this is done by automation. But everything changes when a solid fuel boiler is installed in the house. The fuel in it burns unevenly, which leads to cooling or overheating of the heating system. A heat accumulator for heating will help to compensate for these fluctuations and stabilize the temperature in the circuit. A capacious storage tank will be able to retain an excess of thermal energy, gradually giving it to the heating system.
In this review, we will look at:
- How do heat accumulators for heating systems work;
- How to calculate the required volume of the battery tank;
- How are storage tanks connected?
- The most popular models of thermal storage devices.
Let's go through these points in more detail.
The principle of operation of heat accumulators
If you install a solid fuel boiler in the house, there will be a severe need to regularly add new portions of firewood. It's all about the limited volume of the combustion chamber - it cannot accommodate an unlimited number of logs. Yes, and systems for their automatic supply have not yet been invented, if we do not take into account pellet boilers with automation. In other words, you will have to monitor the operation of the heating system yourself.
These boilers develop maximum power at the moment when firewood blazes merrily in them. At this point, they give a lot of extra energy, so users dose the firewood carefully, putting them in one log at a time. Otherwise, the house will be too hot. There is nothing good in this, because because of this, the number of approaches increases, which is already high. The problem is solved with the help of a heat accumulator.
A thermal accumulator for heating is a storage tank in which a hot coolant accumulates. Moreover, energy is given to the heating circuit in a strictly dosed manner, which ensures temperature stability. Due to this, households get rid of temperature fluctuations and frequent approaches for laying firewood. Accumulation tanks are able to accumulate excess heat energy and smoothly release it to the heating circuits.
Let's try to explain the principle of working on the fingers:
The simplicity of the design of the thermal accumulator not only increases the reliability of the unit, but also simplifies repairs and scheduled maintenance.
- The heating boiler installed in the heating system with a heat accumulator is loaded with firewood and produces a large amount of thermal energy;
- The received energy is sent to the thermal battery and accumulates there;
- At the same time, with the help of a heat exchanger, heat is taken in for the heating system.
A buffer tank for heating (aka a heat accumulator) operates in two modes - accumulation and return. In this case, the power of the boiler may exceed the required heat output for heating the home. While firewood is burning in the firebox, heat will accumulate in the thermal accumulator. After the logs go out, energy will be taken from the battery for a long time.
The heat accumulators of Lazybok for hotbeds and greenhouses are arranged in approximately the same way - during the day they accumulate heat from the sun, and at night they give it away, warming the plants and preventing them from freezing. They just look a little different.
Heat accumulators for heating systems are also necessary if solar panels or heat pumps are used as a heat source. The same batteries cannot provide heat around the clock, since at night their efficiency drops to zero. During daylight hours, they will not only heat the house, but also accumulate thermal energy in the storage tank.
Heat accumulators can be useful when using electric boilers . Such a scheme justifies itself on a two-tariff payment system. In this case, the system is configured so that heat is accumulated at night, and heat is released during the day. Thanks to this, consumers have the opportunity to save money on electricity consumption.
Varieties of heat accumulators
The heat accumulator for the heating system is a capacious tank equipped with solid thermal insulation - it is she who is responsible for minimizing heat loss. With the help of one pair of pipes, the battery is connected to the boiler, and with the help of another pair - to the heating system. Also, additional pipes can be provided here for connecting a DHW circuit or additional sources of thermal energy. Let's look at the main types of heat accumulators for heating systems:

In the presence of a circulation pump, it becomes possible to use several buffer tanks at once, which allows you to evenly heat several rooms at once.
- Buffer tank - is a simple tank, devoid of internal heat exchangers. The design provides for the use of the same coolant in the boiler and batteries, at the same allowable pressure. If it is planned to pass one coolant through the boiler, and another through the batteries, an external heat exchanger should be connected to the heat accumulator;
- Heat accumulators for individual heating with lower, upper or several heat exchangers at once - such heat accumulators allow you to organize two independent circuits. The first circuit is a tank connected to the boiler, and the second is a heating circuit with batteries or convectors. The heat carriers do not mix here, in both circuits there may be different pressures. Heating is carried out using a heat exchanger;
- With a flow heat exchanger of the DHW circuit or with a tank - for organizing hot water supply. In the first case, water can be consumed all day and evenly. The second scheme provides for the accumulation of water in order to quickly return it at a certain time (for example, in the evening, when everyone takes a shower before going to bed) - indirect boilers that accumulate water are arranged in a similar way.
The design of heat accumulators for heating can be very different, the choice of the appropriate option depends on the complexity of the heating system, its characteristics and the number of hot coolant sources.
Some heat accumulators are equipped with heating elements with thermostats, which makes it possible to provide consumers with heat at night, when the coolant has already cooled down, and there is no one to throw firewood into the furnace. They are also useful when using heat pumps and solar panels.
Calculation of the volume of the heat accumulator
We have come close to the most difficult issue - to calculate the required volume of the heat accumulator. To do this, we will use the following formula - m=W/(K*C*Δt). The letter W denotes the amount of excess heat, K is the efficiency of the boiler (indicated as a decimal fraction), C is the heat capacity of water (heat carrier), and Δt is the temperature difference, determined by subtracting the temperature of the heat carrier on the return pipe from the temperature on the supply pipe. For example, it can be 80 degrees at the outlet and 45 degrees at the return - in total we get Δt = 35.
First, let's calculate the amount of excess heat. Suppose that for a house of 100 square meters. m. we need 10 kW of heat per hour. The burning time on one bookmark of firewood is 3 hours, and the boiler power is 25 kW. Consequently, in 3 hours the boiler will generate 75 kW of heat, of which only 30 kW must be sent for heating. In total, we have 45 kW of excess heat left - this is enough for another 4.5 hours of heating. In order not to lose this heat and not to reduce the amount of loaded firewood (otherwise we will simply overheat the system), you should use a heat accumulator.
As for the heat capacity of water, it is 1.164 W * h / kg * ° C - if you do not understand physics, just do not go into details. And remember that if you use a different coolant, then its heat capacity will be different.

Having carried out the necessary calculations, using our advice, you can easily choose a model that most accurately satisfies all your needs.
In total, we have all four values \u200b\u200b- this is 45,000 W of heat, the efficiency of the boiler (suppose 85%, which will be 0.85 in fractional terms), the heat capacity of water is 1.164 and the temperature difference is 35 degrees. We carry out calculations - m \u003d 45000 / (0.85 * 1.164 * 35). With these figures, the volume is 1299.4 liters. We round up and get the capacity of the heat accumulator for our heating system equal to 1300 liters.
If you can’t do the calculations yourself, use special calculators, auxiliary tables or the help of specialists.
Wiring diagrams
The simplest scheme for connecting a heat accumulator to a solid fuel boiler involves the use of the same coolant at equal pressure in the boiler and the heating system. For these purposes, the simplest storage tank without heat exchangers is suitable. Two pumps are installed on the return pipes - by adjusting their performance, we will ensure temperature control in the heating system. There is a similar scheme using a three-way valve - it allows you to control the temperature by mixing the hot coolant and the cooled coolant from the return pipe.
Heat accumulators with a built-in heat exchanger are designed to work in heating systems with high heat carrier pressure. To do this, heat exchangers are located inside them, connected through a circulation pump to the boilers - this is how a supply circuit is formed. The internal capacity of the storage tank with a second circulation pump and batteries forms a heating circuit. Both circuits can circulate different heat transfer fluids, such as water and glycol.
The scheme of a solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator and a DHW circuit allows for the supply of hot water without the use of double-circuit equipment. For this, internal flow heat exchangers or built-in tanks are used. If hot water is needed throughout the day, we recommend buying and installing a heat accumulator with a flow exchanger. For peak one-time consumption, batteries with hot water tanks are optimal.
Bivalent and multivalent connection schemes have also been developed - they provide for the use of several heat sources at once for heating operation. For this, heat accumulators with several heat exchangers can be used.
Popular Models
It's time to deal with the most popular models of heat accumulators for heating systems. We will consider the products of domestic and foreign manufacturers.

The manufacturer of Prometheus heat accumulators is the Novosibirsk company SibEnergoTerm. It produces models with a volume of 230, 300, 500, 750 and 1000 liters. The equipment warranty is 5 years. Heat accumulators are endowed with four outlets for connection to heating and heat sources. For the conservation of the accumulated energy, a layer of thermal insulation made of mineral wool is responsible. Working pressure is 2 atm., Maximum - 6 atm. When buying equipment, consider its dimensions - for example, the diameter of a 1000-liter model is 900 mm, which is why its body may not fit in standard doorways 80 cm wide.
The price of the presented heat accumulator for heating systems varies in the range from 65 to 70 thousand rubles.

Another capacious heat accumulator for 1000 liters of water. It is equipped with one or two smooth-tube heat exchangers, but lacks thermal insulation, which must be taken into account when installing it - it will have to be purchased separately. The case diameter is 790 mm, but if thermal insulation is added to it, then the diameter grows to 990 mm. The maximum temperature in the heating system is +110 degrees, in the DHW circuit - up to +95 degrees.

These heat accumulators are represented by modifications with six or ten connections. There are also terminals for temperature sensors on board. The capacity of the tanks is 960 liters, the working pressure is up to 3 bar. The thickness of the heat-insulating layer is 80 mm. The use of other liquids as a heat carrier, except for water, is not allowed - this applies to both circuits, and not just the heating circuit. If necessary, it is possible to connect several heat accumulators in series into a single cascade.
Homemade heat accumulators
Nothing prevents you from assembling a heat accumulator for a heating system with your own hands - for this you need to make calculations and draw a drawing, focusing on the required capacity. Tanks are constructed from sheet metal 1-2 mm thick, cut with a plasma cutter, cutting machine or welding machine. Heat exchangers are organized from metal straight or corrugated pipes. And in order to avoid rapid corrosion of the metal, it is necessary to purchase a magnesium anode. Basalt wool can be used as thermal insulation.

As a bonus, we present a detailed drawing of a heat accumulator with a capacity of 500 liters - this is enough to maintain the heating system in a small house.
Video
A heat accumulator (TA, buffer tank) is a device that provides the accumulation and preservation of heat for a long time for its further use. The simplest example of a heat storage device is an ordinary household thermos. As another example, we can name a conventional brick oven, which heats up when fuel is burned in it, and after the end of the furnace, the oven continues to give off heat for several hours, heating the room.
The use of a buffer tank in heating and hot water systems ensures uninterrupted supply of heated coolant to heating devices whether the boiler is currently running or not.
The heat accumulator also makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the entire system, increase the resource of the equipment and significantly reduce the consumption of energy resources for space heating and hot water supply.
The greatest effect from the use of TA is noticeable in a system operating on the basis of a solid fuel heating boiler. This allows you to achieve significant fuel savings (up to 25-30%) and increase the boiler efficiency up to 85%.
You can buy a ready-made battery tank in the store or make it yourself. At the same time, it is important to correctly calculate its capacity and other technical parameters, as well as correctly connect the buffer storage tank to the heating system.
In this article:
Design features of the heat accumulator

Drawing of a storage tank
The main element of any TA is a thermal storage material with a high heat capacity.
Depending on the type of material used, heat accumulators for a boiler can be:
- solid state;
- liquid;
- steam;
- thermochemical;
- with an additional heating element, etc.
For heating and hot water supply of private houses, hot water storage tanks are used, where it is water with a high specific heat capacity that acts as a thermal storage element.
Instead of water, it is sometimes used, intended for home heating systems.
An example of a water heater with an additional electric heating element for a hot water supply system is a modern storage water heater.
A conventional thermal energy accumulator is a sealed metal tank of various volumes (from 200 to 5000 liters or more), as a rule, of a cylindrical shape, enclosed in an outer shell (case).
Between the tank and the outer shell there is an insulating layer of heat-insulating material.
In the upper and lower parts of the tank there are two branch pipes for connecting to the heating boiler and to the heating system itself.
At the bottom there is usually a drain valve for draining the liquid, and at the top there is a safety valve for automatic bleeding of air when the pressure inside the buffer tank rises. There may also be flanges for connecting pressure and temperature sensors (thermometer).

Tubular electric heaters
Sometimes inside the buffer tank one or more additional heaters can be installed different type:
- electric heater (TEN);
- and / or a heat exchanger (coil) connected to additional heat sources (solar collectors, heat pumps, etc.).
The main task of these heaters is to maintain the required heating temperature of the working fluid inside the HE.
Also, a DHW heat exchanger can be located inside the tank, which provides hot water by heating it with the working fluid of the heating system.
The principle of operation of the storage tank

Heating circuit with a heat accumulator
The principle of operation of TA for a solid fuel boiler is based on the high specific capacity of the working fluid (water or antifreeze). By connecting the tank, the volume of liquid increases several times, as a result of which the inertia of the system increases.
At the same time, the coolant heated to the maximum by the boiler retains its temperature in the HE for a long time, flowing as necessary to the heating devices.
This ensures continuous operation of the heating system even when the combustion of fuel in the boiler stops.
Consider how the system works with solid fuel boiler and forced coolant supply.
To start the system, the circulation pump installed in the pipeline between the boiler and the heat accumulator is turned on.
The cold working fluid from the lower part of the HE is fed into the boiler, heated in it, and enters its upper part.
Due to the fact that the specific gravity of hot water is less, it practically does not mix with cold water and remains in the upper part of the buffer tank, gradually filling its internal space due to cold water being pumped into the boiler.
When the circulation pump installed in the return line of the system between the heating devices and the storage tank is turned on, the cold coolant begins to flow into the lower part of the HE, displacing hot water from its upper part into the supply line.
In this case, the hot working fluid flows to all heating devices.
The required amount of heat for space heating can be automatically regulated by a room temperature sensor that controls the operation of a three-way valve installed at the TA outlet in the supply line. When the set temperature in the room is reached, the sensor sends a control signal to the valve, which is triggered and limits the supply of hot coolant to the system, redirecting it back to the heat exchanger.
After the combustion of fuel in the boiler, the hot coolant from the storage tank continues to flow into the system as needed until the cooled working fluid from the return line completely fills its internal volume.

DHW scheme with storage tank
TA working hours when the boiler is not working, it can be quite a long time. It depends on the outdoor temperature, the volume of the buffer tank and the number of heaters in the heating system.
To preserve heat inside the heat accumulator, the tank is thermally insulated.
Also, additional heat sources can be used for this in the form of built-in electric heaters (heaters) and / or heat carriers (coils) connected to other heat sources (electric and gas boilers, solar collector, etc.).
The DHW coolant built into the tank provides heating of cold water supplied through it from the plumbing system. Thus, it plays the role of a flowing water heater, providing the needs of the owners of the house for hot water.
Connection (piping) of the heat accumulator to the heating system
As a general rule, the buffer tank is connected to the heating system in parallel with the heating boiler, so this circuit is also called a boiler.
Let us give the usual scheme for connecting TA to a heating system with a solid fuel heating boiler (to simplify the scheme, shutoff valves, automation, control devices and other equipment are not indicated on it).

Simplified heat accumulator piping scheme
This diagram shows the following elements:
- Heating boiler.
- Thermal accumulator.
- Heating devices (radiators).
- Circulation pump in the return line between the boiler and the heater.
- Circulation pump in the return line of the system between heating devices and TA.
- Heat exchanger (coil) for hot water supply.
- Heat exchanger connected to an additional heat source.
One of the upper pipes of the tank (pos. 2) is connected to the boiler outlet (pos. 1), and the second one is connected directly to the heating system supply line.
One of the lower branch pipes of the HE is connected to the boiler inlet, while a pump (pos. 4) is installed in the pipeline between them, which ensures the circulation of the working fluid in a circle from the boiler to the HE and vice versa.
The second lower branch pipe TA is connected to the return line of the heating system, in which a pump (pos. 5) is also installed, which supplies the heated coolant to the heaters.
To ensure the functioning of the heating system in the event of a sudden power outage or failure of the circulation pumps, they are usually connected in parallel to the main line.
In systems with natural coolant circulation, there are no circulation pumps (pos. 4 and 5). This significantly increases the inertia of the system, and at the same time makes it completely non-volatile.
Heat exchanger for domestic hot water(pos. 6) is located in the upper part of the TA.
The location of the additional heat exchanger (pos. 7) depends on the type of heat input source:
- for high-temperature sources (heating element, gas or electric boiler) it is placed in the upper part of the buffer tank;
- for low-temperature ones (solar collector, heat pump) - at the bottom.
The heat exchangers indicated in the diagram are optional (pos. 6 and 7).
What to consider when buying

The choice of heat storage for heating
When choosing a heat accumulator for individual heating of a house, it is necessary to take into account the volume of the tank and its technical parameters, which must correspond to the parameters of the boiler and the entire heating system.
These include, in particular:
1. Dimensional dimensions and weight devices that should enable its installation. In the event that it is impossible to find a suitable place in the house for a tank with the required capacity, it is allowed to replace one tank with several smaller buffer tanks.
2. Max pressure working fluid in the heating system. The shape of the buffer tank and the thickness of its walls depend on this value. With a system pressure of up to 3 bar, the shape of the tank does not really matter, but with a possible increase in this value to 4-6 bar, it is necessary to use toroidal containers (with spherical lids).
3. Maximum allowable temperature working fluid for which the TA is designed.
4. Material storage tank for the heating system. They are usually made of carbon mild steel with a moisture resistant coating or stainless steel. Stainless steel containers are distinguished by the highest anti-corrosion properties and durability in operation, although they are more expensive.
5. Availability or ability to install:
- electric heaters (heaters);
- built-in heat exchanger for connection to hot water supply, which provides hot water supply to the house without additional water heaters;
- additional built-in heat exchangers for connection to other heat sources.
Comparison of popular models
Many domestic and foreign manufacturers are engaged in the production of heat storage tanks. Here is a comparative table of some models of Russian and foreign models with a capacity of 500 liters.
| Model | NIBE BU-500.8 | reflex PFH-500 | ACV AK 500 | Meibes PSX-500 | Sibenergo-term | PROFBAK TA-BB-500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producing country | Sweden | Germany | Belgium | Germany | Russia | Russia |
| Tank volume, l. | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Height, mm | 1757 | 1946 | 1790 | 1590 | 2000 | 1500 |
| Diameter, mm | 750 | 597 | 650 | 760 | 700 | 650 |
| Weight, kg | 145 | 115 | 150 | 120 | 165 | 70 |
| Max working pressure, bar | 6 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 3 |
| Max operating temperature, °C | 95 | 95 | 90 | 95 | 90 | 90 |
| DHW connection | option | No | No | No | No | option |
| Additional heating | option | No | option | No | No | Heating element 1.5 kW |
| Approximate cost, rub. | 43 200 | 35 100 | 53 200 | 62 700 | 28 500 | 55 800 |
This table clearly shows that the price of a storage tank for heating with approximately the same parameters can be in a fairly wide range.
The cost mainly depends on the material (carbon steel or stainless steel), its shape (regular or toroidal), as well as the availability of additional options or the ability to install them.
Tank Volume Calculation

The main parameter when buying a buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler, as well as for is the capacity of the heat accumulator, which directly depends on the power of the heating boiler.
There are various calculation methods based on determining the ability of a solid fuel boiler to heat the required volume of working fluid to a temperature of at least 40 ° C during the combustion of one full load of fuel (approximately 2-3.5 hours).
Compliance with this condition allows you to get the maximum efficiency of the boiler with maximum fuel economy.
The easiest way to calculate provides that one kilowatt of boiler power must correspond to at least 25 liters of the volume of the buffer tank connected to it.
Thus, with a boiler power of 15 kW, the capacity of the storage tank must be at least: 15 * 25 \u003d 375 liters. At the same time, it is better to choose a container with a margin, in this case - 400-500l.
There is also such a version: the larger the tank capacity, the more efficient the heating system will work and the more fuel will be saved. However, this version imposes limitations: the search for free space in the house for the installation of a large heat accumulator, as well as the technical capabilities of the heating boiler itself.
The volumes of the coolant tank have an upper limit: no more than 50 liters per 1 kW. Thus, the maximum volume of the storage tank with a boiler power of 15 kW should not exceed: 15 * 50 \u003d 750 liters.
It is obvious that the use of 1000 liters or more TA for a 10 kW boiler will cause additional fuel consumption to heat such a volume of working fluid to the desired temperature.
This will lead to a significant increase in the inertia of the entire heating system.
 To provide a home boiler room with environmentally friendly fuel, we recommend learning how to make.
To provide a home boiler room with environmentally friendly fuel, we recommend learning how to make.
Solid fuel boilers are more difficult to switch to automatic operation. Such "smart" electrical devices as the GSM module help to make the heating system more or less self-regulating. Go to .
Advantages and disadvantages of buffer capacity

Boiler buffer tank
The main advantages of a heating system with a heat accumulator include:
- the maximum possible increase in the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler and the entire system while saving energy resources;
- ensuring protection of the boiler and other equipment from overheating;
- ease of use of the boiler, allowing it to be loaded at any time;
- automation of the boiler operation through the use of temperature sensors;
- the ability to connect several different heat sources to the HE (for example, two boilers of various types), ensuring their integration into one heating system circuit;
- ensuring a stable temperature in all rooms of the house;
- the possibility of providing domestic hot water without the use of additional water heating devices.
The disadvantages of heat accumulators for the heating system include:
- increased inertia of the system (much more time passes from the moment the boiler is ignited until the system enters the operating mode);
- the need to install TA near the heating boiler, for which a separate room of the required area is required in the house;
- large dimensions and weight, causing the complexity of its transportation and installation;
- a rather high cost of industrially produced HE (in some cases, its price, depending on the parameters, may exceed the cost of the boiler itself).
An interesting solution: a heat accumulator in the interior of the house.
 In the interior
In the interior  Installation
Installation 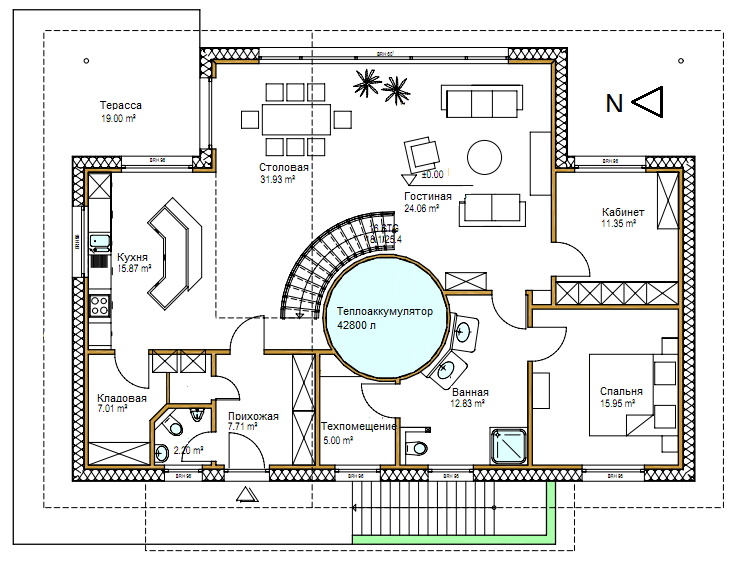 1st floor
1st floor  Attic
Attic  Basement
Basement 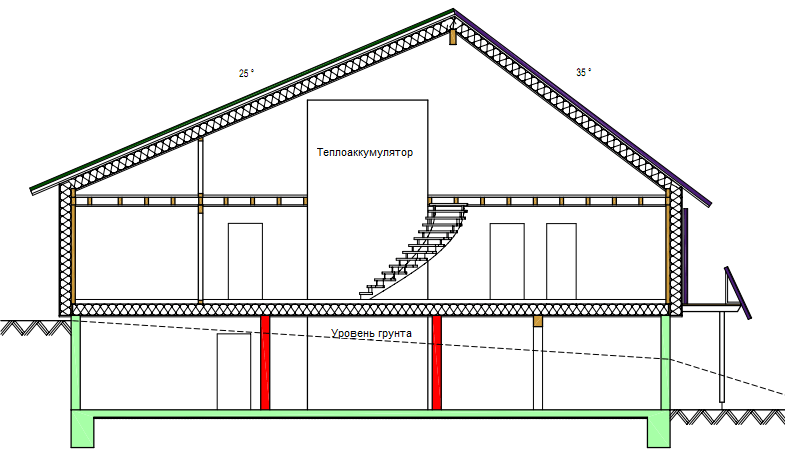 cross section
cross section
The use of a heat accumulator is economically beneficial not only for solid fuel boilers, but also for electric or gas heating systems.
In the case of an electric boiler, The TA is turned on at full power at night, when electricity tariffs are much lower. During the day, when the boiler is turned off, the space is heated using the heat accumulated during the night.
For gas boilers savings are achieved through the alternate use of the boiler itself and TA. At the same time, the gas burner turns on much less frequently, which provides less.
It is undesirable to install a heat accumulator in heating systems where fast and or short-term heating of the room is required, since this will be hampered by the increased inertia of the system.
Often, homeowners are not able to buy modern heating equipment, so they are looking for alternative solutions. Take at least a buffer tank (otherwise - a heat accumulator), an indispensable thing for heating systems with a solid fuel boiler. A storage tank with a volume of 500 liters costs about 600-700 USD. That is, the price of a thousand-liter barrel reaches 1000 USD. e. If you make a heat accumulator with your own hands, and then install the tank in the boiler room yourself, you will be able to save half the indicated amount. Our task is to tell about the manufacturing methods.
Where is the heat accumulator used and how is it arranged
The thermal energy storage is nothing more than an insulated iron tank with branch pipes for connecting water heating mains. The buffer tank performs 2 functions: it accumulates excess heat and heats the house during periods when the boiler is inactive. The heat accumulator replaces the heating unit in 2 cases:
- When heating a dwelling or a boiler that burns solid fuel. The storage tank works for heating at night, after burning firewood or coal. Thanks to this, the homeowner rests calmly, and does not run to the boiler room. It is comfortable.
- When the source of heat is an electric boiler, and electricity consumption is accounted for by a multi-tariff meter. Energy at the night rate is half the price, so during the day the operation of the heating system is fully provided by the heat accumulator. It's economical.
An important point. Tank - hot water accumulator increases the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler. After all, the maximum efficiency of the heat generator is achieved with intense combustion, which cannot be constantly maintained without a buffer tank that absorbs excess heat. The more efficiently firewood is burned, the less their consumption. This also applies to a gas boiler, whose efficiency decreases in low combustion modes.
An accumulator tank filled with coolant operates according to a simple principle. While the heat generator is engaged in space heating, the water in the tank is heated to a maximum temperature of 80-90 ° C (the heat accumulator is charging). After the boiler is turned off, hot coolant is supplied to the radiators from the storage tank, which provides heating for the house for a certain time (the heat battery is discharged). The duration of operation depends on the volume of the tank and the air temperature outside.
 How does a factory-made heat accumulator work?
How does a factory-made heat accumulator work? The simplest prefabricated water storage tank shown in the diagram consists of the following elements:
- the main tank is cylindrical, made of carbon or stainless steel;
- heat-insulating layer with a thickness of 50-100 mm, depending on the insulation used;
- outer skin - thin painted metal or polymer case;
- connecting fittings embedded in the main tank;
- immersion sleeves for mounting a thermometer and pressure gauge.
Note. More expensive models of heat accumulators for heating systems are additionally supplied with coils for hot water supply and heating from solar collectors. Another useful option is a block of electric heating elements built into the upper zone of the tank.
Production of heat accumulators in the factory
If you are seriously concerned about installing a heat accumulator and decide to make it on your own, then first you should familiarize yourself with the factory assembly technology.
 Cutting blanks for the lid and bottom on a plasma machine
Cutting blanks for the lid and bottom on a plasma machine It is unrealistic to repeat the technological process in a home workshop, but some tricks will come in handy. At the enterprise, the hot water storage tank is made in the form of a cylinder with a hemispherical bottom and a lid in the following order:
- Sheet metal 3 mm thick is fed to the plasma cutting machine, where it is used to produce blanks for end caps, body, hatch and stand.
- On a lathe, main fittings with a diameter of 40 or 50 mm (thread 1.5 and 2”) and immersion sleeves for control devices are manufactured. A large flange for an inspection hatch about 20 cm in size is also machined there. A branch pipe is welded to the latter for inserting into the body.
- The blank body (the so-called shell) in the form of a sheet with holes for fittings is sent to the rollers, bending it under a certain radius. To get a cylindrical water tank, it remains only to weld the ends of the workpiece end-to-end.
- From metal flat circles, a hydraulic press stamps hemispherical caps.
- The next operation is welding. The order is as follows: first, the body is boiled on the tacks, then the covers are tacked to it, then all the seams are completely welded. At the end, fittings and an inspection hatch are attached.
- The finished storage tank is welded to the stand, after which it passes 2 permeability tests - air and hydraulic. The latter is produced with a pressure of 8 bar, the test lasts 24 hours.
- The tested tank is painted and insulated with basalt fiber at least 50 mm thick. From above, the container is sheathed with thin-sheet steel with a polymeric color coating or closed with a tight cover.
 The body of the drive is bent from a sheet of iron on rollers
The body of the drive is bent from a sheet of iron on rollers Reference. To insulate the tank, manufacturers use different materials. For example, Russian-made Prometheus heat accumulators are insulated with polyurethane foam.
 Instead of cladding, manufacturers often use a special cover (you can choose a color)
Instead of cladding, manufacturers often use a special cover (you can choose a color) Most factory-made heat accumulators are designed for a maximum pressure of 6 bar at a coolant temperature in the heating system of 90 °C. This value is twice the threshold of the safety valve installed on the safety group of solid fuel and gas boilers (limit - 3 bar). The production process is shown in detail in the video:
We make a thermal battery ourselves
You have decided that you cannot do without a buffer tank and want to make it yourself. Then get ready to go through 5 stages:
- Calculation of the volume of the heat accumulator.
- Choosing the right design.
- Selection and preparation of materials.
- Assembly and leak test.
- Installation of the tank and connection to the water heating system.
Advice. Before calculating the volume of the barrel, think about how much space in the boiler room you can allocate for it (in terms of area and height). Clearly determine how long the water heat accumulator should replace the inactive boiler, and only then proceed with the first stage.
How to calculate tank volume
There are 2 ways to calculate the storage tank capacity:
- simplified, offered by manufacturers;
- accurate, performed according to the formula for the heat capacity of water.
 The duration of heating a house with a heat accumulator depends on its size.
The duration of heating a house with a heat accumulator depends on its size. The essence of the enlarged calculation is simple: for each kW of power of the boiler plant, a volume equal to 25 liters of water is allocated in the tank. Example: if the capacity of the heat generator is 25 kW, then the minimum capacity of the heat storage will be 25 x 25 = 625 l or 0.625 m³. Now remember how much space is allocated in the boiler room and adjust the resulting volume to the actual size of the room.
Reference. Those who want to weld a home-made heat accumulator often wonder how to calculate the volume of a round barrel. Here it is worth recalling the formula for calculating the area of a circle: S = ¼πD². Substitute the diameter of the cylindrical tank (D) into it, and multiply the result by the height of the tank.
You will get more accurate dimensions of the heat accumulator if you use the second method. After all, a simplified calculation will not show how long the calculated amount of coolant will last under the most adverse weather conditions. The proposed methodology just dances from the indicators that you need and is based on the formula:
m = Q / 1.163 x Δt
- Q is the amount of heat that needs to be stored in the battery, kWh;
- m is the calculated mass of the coolant in the tank, tons;
- Δt is the difference in water temperatures at the beginning and at the end of heating;
- 1.163 Wh/kg °C is the reference heat capacity of water.

Let's explain further with an example. Let's take a standard house of 100 m² with an average heat consumption of 10 kW, where the boiler must stand idle for 10 hours a day. Then it is necessary to accumulate 10 x 10 = 100 kWh of energy in the barrel. The initial water temperature in the heating network is 20 °C, heating occurs up to 90 °C. We consider the mass of the coolant:
m = 100 / 1.163 x (90 - 20) = 1.22 tons, which is approximately equal to 1.25m³.
Please note that the heat load of 10 kW is taken approximately; in an insulated building with an area of 100 m², heat loss will be less. The second moment: so much heat is needed on the coldest days, which are 5 for the whole winter. That is, a heat accumulator for 1000 liters is enough with a large margin, and taking into account the seasonal temperature difference, you can safely keep within 750 liters.
Hence the conclusion: in the formula you need to substitute the average heat consumption for the cold period, equal to half of the maximum:
m = 50 / 1.163 x (90 - 20) = 0.61 tons or 0.65 m³.
Note. If you calculate the volume of the barrel according to the average heat consumption, in severe frosts it will not be enough for the estimated period of time (in our example, 10 hours). But save money and space in the furnace room. More information on conducting calculations is presented in.
About tank design
In order to make a heat accumulator yourself, you will have to defeat one insidious enemy - the pressure exerted by the liquid on the walls of the vessel. Do you think why factory tanks are made cylindrical, and the bottom with a lid is hemispherical? Yes, because such a container is able to withstand the pressure of hot water without additional reinforcement.
On the other hand, few people have the technical ability to mold metal on rollers, not to mention the drawing of semicircular parts. We offer the following solutions to the issue:
- Order a round inner tank at a metalworking company, and carry out the insulation and final installation work yourself. It will still cost less than buying a factory-assembled heat accumulator.
- Take a ready-made cylindrical tank and make a buffer tank on its base. Where to get such tanks, we will tell you in the next section.
- Weld a rectangular heat accumulator from sheet iron and reinforce its walls.
 Sectional drawing of a rectangular heat accumulator with a volume of 500 l
Sectional drawing of a rectangular heat accumulator with a volume of 500 l Advice. In a closed heating system with a solid fuel boiler, where the overpressure can rise to 3 bar or more, it is highly recommended to use a cylindrical heat accumulator.
In an open heating system with zero water pressure, a rectangular tank can be used. But do not forget about the hydrostatic pressure of the coolant on the walls, add to it the height of the water column from the tank to the expansion tank installed at the highest point. That is why it is necessary to strengthen the flat walls of a home-made heat accumulator, as shown in the drawing of a 500-liter tank.
A rectangular storage tank, properly reinforced, can also be used in a closed heating system. But in case of an emergency pressure surge due to overheating of the TT boiler, the tank will leak with a probability of 90%, although you may not notice a small crack under the insulation layer. How the non-reinforced metal of the vessel sticks out when filled with water, look at the video:
Reference. It makes no sense to weld directly onto the stiffening walls from corners, channels and other rolled metal. Practice shows that the pressure force bends corners of a small section together with the wall, and tears off large ones along the edges.
Making a powerful frame outside is impractical, too much material consumption. A compromise option is the internal spacers shown on the drawing of a home-made heat accumulator.
 Drawing of a heat accumulator for 500 l - top view (cross section)
Drawing of a heat accumulator for 500 l - top view (cross section) Selection of materials for the tank
You will greatly facilitate your task if you find a ready-made cylindrical tank, originally designed for a pressure of 3–6 bar. What containers can be used:
- propane cylinders of various capacities;
- decommissioned process tanks, for example, receivers from industrial compressors;
- receivers from railway cars;
- old iron boilers;
- internal tanks for storage of liquid nitrogen, made of stainless steel.
 It is much easier to make a reliable heat accumulator from ready-made steel vessels
It is much easier to make a reliable heat accumulator from ready-made steel vessels Note. In extreme cases, a steel pipe of a suitable diameter will do. Flat covers can be welded to it, which will have to be reinforced with internal stretch marks.
To weld a square tank, take sheet metal 3 mm thick, no more. Make stiffeners from round pipes Ø15-20 mm or profiles 20 x 20 mm. Choose the size of the fittings according to the diameter of the boiler outlet pipes, and for lining, buy thin steel (0.3-0.5 mm) with powder coating.
A separate question is how to insulate a heat accumulator welded with your own hands. The best option is basalt wool in rolls with a density of up to 60 kg / m³ and a thickness of 60-80 mm. Polymers such as polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam should not be used. The reason is that mice that love warmth and in the fall can easily settle under the lining of your storage tank. Unlike polymeric heaters, they do not gnaw basalt fiber.
 Be under no illusions about extruded polystyrene foam, rodents eat it too
Be under no illusions about extruded polystyrene foam, rodents eat it too Now we will indicate other options for ready-made vessels that are not recommended for use in heat accumulators:
- An impromptu tank from the eurocube. Such plastic containers are designed for a maximum temperature of the contents of 70 ° C, and we need 90 ° C.
- Heat accumulator from an iron barrel. Contraindications - thin metal and flat tank covers. Than to strengthen such a barrel, it is easier to take a good steel pipe.
Assembly of a rectangular heat accumulator
We want to warn you right away: if you are mediocre in welding, then it is better to order the manufacture of the tank on the side according to your drawings. The quality and tightness of the seams is of great importance; at the slightest leak, the storage tank will leak.
 First, the tank is assembled on tacks, and then boiled with a continuous seam
First, the tank is assembled on tacks, and then boiled with a continuous seam For a good welder, there will be no problems here, you just need to learn the order of operations:
- Cut blanks from metal to size and weld the body without a bottom and a lid on tacks. To fix the sheets, use clamps and a square.
- Cut holes in the side walls for stiffeners. Insert the prepared pipes inside and scald their ends from the outside.
- Grab the bottom with a lid to the tank. Cut holes in them and repeat the operation with the installation of internal stretch marks.
- When all opposite walls of the container are securely connected to each other, begin continuous welding of all seams.
- Install supports from pipe sections at the bottom of the tank.
- Insert the fittings, stepping back from the bottom and cover by less than 10 cm, as shown in the photo below.
- Weld metal brackets to the walls, which will serve as brackets for fastening the heat-insulating material and sheathing.
 The photo shows a stretch from a wide strip, but it is better to use a pipe
The photo shows a stretch from a wide strip, but it is better to use a pipe Advice on mounting internal spacers. In order for the walls of the heat accumulator to effectively resist bending and not break off by welding, extend the ends of the braces outward by 50 mm. Then additionally weld stiffeners to them from a steel sheet or strip. Do not worry about the appearance, the ends of the pipes will then hide under the cladding.
 Steel brackets (clips) are welded to the body for fixing insulation and cladding
Steel brackets (clips) are welded to the body for fixing insulation and cladding A few words about how to insulate the heat accumulator. First, check it for leaks by filling it with water or smearing all the seams with kerosene. Thermal insulation is quite simple:
- clean and degrease all surfaces, apply a primer and paint to them in order to protect against corrosion;
- wrap the tank with insulation without squeezing it, and then secure it with a cord;
- cut the facing metal, make holes in it for the pipes;
- fasten the casing to the brackets with self-tapping screws.
Screw the cladding sheets so that they are interconnected with fasteners. This completes the manufacture of a home-made heat accumulator for an open heating system.
Installation and connection of the tank to heating
If the volume of your heat accumulator exceeds 500 liters, then it is undesirable to put it on a concrete floor, it is better to arrange a separate foundation. To do this, dismantle the screed and dig a hole to a dense layer of soil. Then fill it with broken stone (but), compact and fill with liquid clay. From above, pour a reinforced concrete slab 150 mm thick in a wooden formwork.
 Scheme of the foundation device for the battery tank
Scheme of the foundation device for the battery tank The correct operation of the heat accumulator is based on the horizontal movement of hot and cooled flow inside the tank when the battery is "charged", and the vertical flow of water during the "discharge". To organize such battery operation, you need to perform the following activities:
- the circuit of a solid fuel or other boiler is connected to a water storage tank through a circulation pump;
- the heating system is supplied with a coolant using a separate pump and a mixing unit with a three-way valve that allows you to take the required amount of water from the battery;
- the pump installed in the boiler circuit should not be inferior in performance to the unit supplying the coolant to the heating appliances.
 Tank piping scheme - heat accumulator
Tank piping scheme - heat accumulator The standard connection diagram for a heat storage tank with a TT boiler is shown in the figure above. The balancing valve on the return is used to regulate the flow of the coolant according to the temperature of the water at the inlet and outlet of the tank. Our expert Vladimir Sukhorukov will tell you how to properly strap and set up in his video:
Reference. If you live in the capital of the Russian Federation or the Moscow region, then on the issue of connecting any heat accumulators, you can consult personally with Vladimir using the contact details on his official website.
Budget accumulating tank from cylinders
For those homeowners who have a very limited boiler room area, we suggest making a cylindrical heat accumulator from propane cylinders.
 Homemade heat storage paired with a TT boiler
Homemade heat storage paired with a TT boiler The 100 l design, developed by our other master -, is designed to perform 3 functions:
- unload the solid fuel boiler in case of overheating, absorbing excess heat;
- heat water for household needs;
- provide heating of the house for 1-2 hours in case of attenuation of the TT-boiler.
Note. The battery life of the heat accumulator is short due to its small volume. But it will fit in any furnace room and will be able to remove heat from the boiler after a power outage, since it is connected directly, without a pump.
 It looks like an unlined tank made of cylinders
It looks like an unlined tank made of cylinders To assemble the storage tank you will need:
- 2 standard propane tanks;
- at least 10 m of copper tube Ø12 mm or stainless corrugation of the same diameter;
- fittings and sleeves for thermometers;
- insulation - basalt wool;
- painted metal for sheathing.
From the cylinders, you need to unscrew the valves and cut off the covers with a grinder, filling them with water to prevent the explosion of gas residues. We carefully bend the copper tube into a coil around another pipe of a suitable diameter. Then we proceed like this:
- Using the presented drawing, drill holes in the future heat accumulator for pipes and thermometer sleeves.
- Fasten by welding inside the cylinders several metal brackets for mounting the DHW heat exchanger.
- Put the cylinders one on top of the other and weld together.
- Install a coil inside the resulting tank, releasing the ends of the tube through the holes. Use gland packing to seal these places.
- Attach the bottom and lid.
- Insert an air outlet into the lid, and a drain valve into the bottom.
- Weld the brackets for attaching the skin. Make them of different lengths so that the finished product has a rectangular shape. It will be inconvenient to bend the lining in a semicircle, and it will not be aesthetically pleasing.
- Insulate the tank and screw the casing with self-tapping screws.
 Docking a tank with a TT boiler without a circulation pump
Docking a tank with a TT boiler without a circulation pump The design feature of this heat accumulator is that it is connected to a solid fuel boiler directly, without a circulation pump. Therefore, steel pipes Ø50 mm laid with a slope are used for docking, the coolant circulates by gravity. To supply water to heating radiators, a pump + three-way mixing valve is installed after the buffer tank.
Conclusion
On many Internet resources there is a statement that making a heat accumulator with your own hands is a trifling matter. If you study our material, you will understand that such statements are far from reality, in fact, the issue is quite complex and serious. You can’t just take a barrel and attach it to a solid fuel boiler. Hence the advice: think carefully about all the nuances before starting work. And without the qualification of a welder, it is not worth taking on a buffer tank, it is better to order it in a specialized workshop.
Read also...
- Education of the USSR: prerequisites, stages, significance When the USSR was created
- Education of the USSR: briefly about everything What led to the formation of the USSR
- Socialist-Revolutionary Party: who are they? Their goals and program. Political parties at the beginning of the 20th century Socialist-Revolutionaries party program table briefly
- Vitaprost rectal suppositories: how to use the drug correctly You can take Vitaprost without a doctor's prescription


















