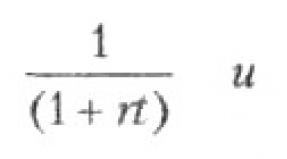Optimal coolant temperature in a private house. Optimal coolant temperature in a private house Thermal mode of the boiler
05.09.2018
They are almost never equipped with circulation pumps, a safety group, or adjustment and control devices. Everyone solves these issues independently, choosing a heating device piping scheme in accordance with the type and features of the heating system. Not only the efficiency and performance of heating, but also its reliable, trouble-free operation depends on how correctly the heat generator is installed. That is why it is important to include in the diagram components and devices that will ensure the durability of the heating unit and its protection in the event of emergency situations. In addition, when installing a solid fuel boiler, you should not give up equipment that creates additional convenience and comfort. Using a heat accumulator, you can solve the problem of temperature differences when rebooting the boiler, and an indirect heating boiler will provide the house with hot water. Have you thought about connecting a solid fuel heating unit according to all the rules? We will help you with this!
However, if the rooms warm up after this, hydraulic adjustment is recommended in connection with updating the heating system. Hydraulic adjustment is especially useful when using condensing boilers. These devices only operate at their highest possible efficiency if the return temperature is below the temperature at which water condenses from the boiler flue gas. Special cases are single pipe systems heating, especially in apartment buildings, as well as buildings with underfloor heating or mixed underfloor heating and radiator heating.
Typical wiring diagrams for solid fuel boilers
The complexity of controlling the combustion process in solid fuel boilers leads to high inertia of the heating system, which negatively affects the convenience and safety during operation. The situation is further complicated by the fact that the efficiency of units of this type directly depends on the temperature of the coolant. For efficient work heating piping must ensure the temperature of the thermal agent within 60 - 65 °C. Of course, if the equipment is not integrated correctly, such heating at above-zero temperatures “overboard” will be very uncomfortable and uneconomical. In addition, the full operation of the heat generator depends on a number of additional factors - the type of heating system, the number of circuits, the presence of additional energy consumers, etc. The wiring diagrams presented below take into account the most common cases. If none of them meets your requirements, then knowledge of the principles and structural features of heating systems will help in developing an individual project.
Hydraulic adjustment can also be done using these heating systems in principle, but usually involves much higher costs. Accurate determination of the boiler characteristics of a heating system is only possible if the heat loss of a structural furnace can be relatively labor-intensive. This calculation of heat load ≡ Heating load ≡ Heating load is the heating power that must be constantly supplied to the room to maintain the temperature in the space, so it must be as large as the sum of heat loss from conduction and ventilation.
Open type system with natural circulation in a private house First of all, it should be noted that open gravity-type systems are considered the most suitable for solid fuel boilers. This is due to the fact that even in emergency cases associated with a sharp increase in temperature and pressure, the heating will most likely remain sealed and operational. It is also important that the functionality of the heating equipment does not depend on the availability of power. Considering that wood-burning boilers are installed not in megacities, but in areas remote from the benefits of civilization, this factor will not seem so insignificant to you. Of course, this scheme is not without its drawbacks, the main ones being:
The valuation should be made on the basis of clear rules, for example, according to comparable values for rooms relating to previous years or comparable premises in the relevant reporting period. In this case, all heating costs are distributed according to a fixed scale, usually by square meter. from experience. Calculation regulation.
What is the required boiler output? For example, by using subsequent thermal insulation ≡ Thermal insulation ≡ Thermal insulation reduces the heat flow from the hot to the cold side of the component. For this purpose, substances with low thermal conductivity are introduced as a layer between hot and cold. Important water retention is achieved using a vacuum. In addition, sleeping air retains heat flow very well.
- free access of oxygen to the system, which causes internal corrosion of pipes;
- the need to replenish the coolant level due to its evaporation;
- uneven temperature of the thermal agent at the beginning and end of each circuit.
A layer of any mineral oil 1 - 2 cm thick, poured into the expansion tank, will prevent oxygen from entering the coolant and reduce the rate of evaporation of the liquid. Despite its shortcomings, the gravity scheme is very popular due to its simplicity, reliability and low cost.
Overestimation is not harmful for oil or gas condensing boilers and may even make sense in some cases. For low temperature boilers ≡ Low temperature boilers ≡ A low temperature boiler is a boiler that can also be used in continuous operation with a low heating water inlet temperature of 35 to 40 degrees Celsius and in which this may cause condensation in the exhaust gases containing water vapor. The standard utilization rate of low temperature boiler is more than 90%.
Condensing heaters achieve an even greater degree of standard efficiency at 100%. Over-measuring should be avoided. To provide secure deletion exhaust gases from the heating system, the heating and the chimney must coincide with each other. Previously, the interaction between the boiler and the chimney was much less important. Adapting the chimney to the boiler was in the background. The high flue gas temperatures of boilers at that time also ensured that the flue gases were discharged without damage, even in the case of large chimney cross-sections, and that the chimney was dry.
When deciding to install using this method, keep in mind that for normal coolant circulation, the boiler inlet must be at least 0.5 m below the heating radiators. The supply and return pipes must have slopes for normal coolant circulation. In addition, it is important to correctly calculate the hydrodynamic resistance of all branches of the system, and during the design process try to reduce the number of shut-off and control valves. The correct operation of a system with natural circulation of coolant also depends on the installation location expansion tank- it must be connected at the highest point.
However, the exhaust gases of modern low-temperature and condensing boilers have very low temperatures due to energy-saving operation. In addition, when replacing an old boiler, the boiler's rated heating output is adapted to the actual, possibly reduced, heating load of the building. This usually results in reduced performance compared to an older, larger boiler. Due to the existing chimney, significantly lower exhaust gas volumes with lower exhaust gas temperatures will be transmitted after replacing the old boiler.
Closed system with natural circulation
Installing a membrane-type expansion tank on the return line will avoid the harmful effects of oxygen and eliminate the need to control the coolant level. When deciding to equip a gravity system with a sealed expansion tank, consider the following points:
Why are chimneys wet? The hot exhaust gas that leaves the boiler combustion chamber contains water vapor. If this exhaust gas is cooled to a certain temperature, the water vapor becomes water and is deposited on cooler surfaces. The temperature of the flue gases in humidified chimneys must be high enough to prevent condensation in the chimney, otherwise moisture or moisture penetration may occur.
The relevant standards and building regulations require precise coordination of the exhaust system with the heat generator. The chimney must be designed and constructed in such a way that exhaust gases can be removed without mechanical assistance, and also to prevent damage to the chimney or the building.
- the capacity of the membrane tank must contain at least 10% of the volume of the entire coolant;
- a safety valve must be installed on the supply pipe;
- the highest point of the system must be equipped with an air vent.
Additional devices that are included in the boiler safety group (safety valve and air vent) will have to be purchased separately - manufacturers very rarely equip units with such devices. The safety valve allows the coolant to be discharged if the pressure in the system exceeds a critical value. A normal operating indicator is considered to be a pressure of 1.5 to 2 atm. The emergency valve is set to 3 atm.
The following requirements for the smoke system must be observed. If the chimney is located on an external wall, there is a risk that the exhaust gas will not receive the necessary thermal buoyancy and that water vapor will condense on the chimney walls. In many cases the existing chimney will be replaced with the above mentioned chimney. no longer meet the requirements.
Every year the chimney cleaner confirms good values exhaust gases. “What more do you need?”, you may wonder. “A whole lot” is our answer. More energy and save more funds for the environment, more comfort, more operational security, more knowledge to trust future security. The deflection of the chimney determines whether the combustion quality and exhaust gas losses during burner operation comply with legal requirements. It checks whether the pipe is working and the system is safe.
Features of systems with forced coolant movement
In order to equalize the temperature in all areas, a circulation pump is integrated into the closed heating system. Since this unit can provide forced movement of the coolant, the requirements for the level of installation of the boiler and compliance with slopes become negligible. However, you should not give up the autonomy of natural heating. If a bypass branch, called a bypass, is installed at the boiler outlet, then in the event of a power outage, the circulation of the thermal agent will be ensured by gravitational forces.
Even if he assures you of ideal values, this does not matter of great importance for the economy of your system. After all, the old boiler must operate constantly at high temperatures all year round. Especially during transition months or even in summer when the boiler is only needed for heating drinking water, high cooling and/or heat is generated, which is typically much higher than the exhaust gas losses measured through the flue.
Not so with the new boiler. Here the boiler water temperature is automatically adjusted to the corresponding outside temperature. If heat is not required, they will even turn off completely. If the boiler is 10 years old or more, it is therefore worth dealing with a new heating system. The new system saves up to 30% in energy and costs. You have a clear advantage in comfort, operational safety, environmental protection and safety to further comply with legal requirements.

The electric pump is installed on the return line, between the expansion tank and the inlet fitting. Thanks to low temperature coolant, the pump operates in a more gentle mode, which increases its durability. Installing a circulation unit on the return line is also necessary for safety reasons. When water boils in the boiler, steam may form, the entry of which into the centrifugal pump can completely stop the movement of the liquid, which can lead to an accident. If the device is installed at the inlet of the heat generator, it will be able to circulate the coolant even in the event of emergency situations.
Operational safety: Heating is only required when necessary
Of course, it would be an exaggeration to think that your old heating system will give up its spirit in the coming days with a big blow. No, if she does, she will probably do it quietly and calmly - without warning. In any case, you can show off new materials and capabilities without any obligation in our showrooms.
Running costs: is it what he wants?
You will notice the high efficiency and long life of the boiler, which is easy to maintain. How much your oil and gas costs, check your bill regularly. It's not easy to see if your heating system is economically viable. It might even generate heat where none is needed: Or it's just oversized.
Connection via manifolds
If it is necessary to connect several parallel branches with radiators, a water heated floor, etc. to a solid fuel boiler, then balancing of the circuits is required, otherwise the coolant will follow the path of least resistance, and the remaining parts of the system will remain cold. For this purpose, one or more collectors (combs) - distribution devices with one input and several outputs - are installed at the outlet of the heating unit. Installation of combs opens up wide possibilities for connecting several circulation pumps, allows you to supply a thermal agent of the same temperature to consumers and regulate its supply. The only disadvantage of this type of piping can be considered the complication of the design and the increased cost of the heating system.
The development of harmful exhaust gases is closely related to consumption and use. Boilers that consume a lot also produce a lot of exhaust gases. Key words: forest death, greenhouse effect. Old boilers use about a third of the fuel and produce more than 60 percent of the pollutants than new boilers.
New burners with modern technology have particularly economical combustion with favorable values, so that they still do not meet the requirements of the Blue Angel ecolabel and the Swiss air pollution regulation.

A separate case of manifold piping is a connection with a hydraulic arrow. Its difference from a conventional collector is that this device acts as a kind of intermediary between the heating boiler and consumers. Made in the form of a pipe large diameter, the hydraulic arrow is installed vertically and connected to the inlet and pressure pipes of the boiler. In this case, consumers are inserted at different heights, which allows you to select the optimal temperature for each circuit.
Operational safety, cost, environment, ease of use. You might be thinking, "Yes, that's it. modern heater, which I already liked." And you may also think: But it's worth it again. After all, it’s not just about buying the purchase price. Then the score looks completely different.
Then you might say, “I can’t save that much.” Be sure to have this account set up for your home by a professional. He also knows financing, for example for solar and condensing technology. What is a refund? Where and why is the technology used? How does reverse flow increase? What are the benefits of heating system efficiency?
Installation of emergency and control systems
Emergency and control systems serve several purposes:
- protection of the system from depressurization in the event of an uncontrolled increase in pressure;
- temperature control of individual circuits;
- boiler protection from overheating;
- prevention of condensation processes associated with large differences in supply and return temperatures.
To solve system safety problems, a safety valve, emergency heat exchanger or natural circulation circuit is introduced into the piping circuit. As for the issues of regulating the temperature of the thermal agent, thermostatic and controlled valves are used for these purposes.
Modern heating systems only operate optimally when certain operating temperatures are not exceeded or exceeded. To prevent excessive cooling of the return, use what is called a return lift. We explain to you in this article what a rollback is and how to technically implement it. You will also find out which heating systems have a reverse rise and which do not.
Free 5 Quotes for your New Heater Request
Functional implementation of reverse flow lift
Reverse lift is a technology used in hot water heating systems to quickly achieve and maintain the desired minimum temperature in the heating circuit heater. The rise of the return flow is achieved through the use of a special mixing valve. This mixes under the cold return a variable portion of the hot heating water that was heated by the heat generator. This usually results in a faster and higher temperature of the coolant returning back to the heat generator.Trim with three-way valve.

A solid fuel boiler is a periodic heating unit, so it is at risk of corrosion due to condensation that falls on its walls during heating. This is due to the ingress of too cold coolant from the return into the heat exchanger of the heating unit. The danger of this factor can be eliminated using a three-way valve. This device is an adjustable valve with two inputs and one output. Based on a signal from the temperature sensor, the three-way valve opens the hot coolant supply channel to the boiler inlet, preventing the formation of a dew point. As soon as the heating unit enters operating mode, the supply of liquid in a small circle stops.
Consequently, the heat exchanger has flow and return flow with a lower temperature difference. The higher temperature of the return flow, which rises in this way, has a positive effect on the operation of the heating system, which can thus function optimally. The optimal operating temperature depends on the fuel being burned, or more precisely on the so-called flue gas dew point.
At the same time, reserve lift is used to counteract damage that may occur, for example, when gases that accumulate during fuel combustion cool down and condense. Condensation can damage the system because it causes effects such as pitting. Temperature differences can also cause stress, leading to cracks.

A fairly common mistake is to install a centrifugal pump before a three-way valve. Naturally, when closed valve There can be no talk of any fluid circulation in the system. It is correct to install the pump after the adjusting device. A three-way valve can also be used to regulate the temperature of the heating agent supplied to consumers. In this case, the device is set to work in the other direction, mixing cold coolant from the return to the supply.
Circuit with buffer capacity

The low controllability of solid fuel boilers requires constant monitoring of the amount of firewood and draft, which significantly reduces the convenience of their operation. Installing a buffer tank (heat accumulator) will allow you to load more fuel without worrying about possible boiling of the liquid. This device is a sealed tank that separates the heating unit from consumers. Due to its large volume, the buffer tank can accumulate excess heat and transfer it to radiators as needed. The mixing unit, which uses the same three-way valve, will help regulate the temperature of the liquid coming from the heat accumulator.
Trim elements ensuring the safety of the heating system

In addition to the safety valve mentioned above, the heating unit is protected from overheating by using an emergency circuit through which cold water from the water supply is supplied to the heat exchanger. Depending on the design of the boiler, the coolant can be supplied directly to the heat exchanger or to a special coil installed in the working chamber of the unit. By the way, it is the last option that is the only possible one for systems with filled antifreeze. The water supply is carried out using a three-way valve, which is controlled by a sensor installed inside the heat exchanger. The “waste” liquid is discharged through a special pipeline connected to the sewer system.
Connection diagram for an indirect heating boiler

Piping with connection of a boiler for hot water supply can be used for heating systems of all types. To do this, a special heat-insulated container (boiler) is connected to the water supply and DHW system, and a coil is installed inside the water heater, which is cut into the heating agent supply line. Passing through this circuit, the hot coolant transfers heat to the water. Often, an indirect heating boiler is also equipped with heating elements, thanks to which it becomes possible to obtain hot water in the warm season.
Correct installation solid fuel boiler into a closed heating system
A huge advantage of solid fuel boilers is that their installation does not require any permits. It is quite possible to carry out the installation yourself, especially since this does not require any special tool, no special knowledge. The main thing is to approach the work responsibly and follow the order of all stages.
Boiler room installation. The disadvantage of heating units used to burn wood and coal is the need for a special, well-ventilated room. Of course, it would be possible to install a boiler in the kitchen or bathroom, however, periodic emissions of smoke and soot, dirt from fuel and combustion products make this idea unsuitable for implementation. In addition, the installation of combustion equipment in living rooms It is also unsafe - the release of fumes can lead to tragedy. When installing a heat generator in a boiler room, several rules are followed:
- the distance from the combustion door to the wall must be at least 1 m;
- ventilation ducts must be installed at a distance no higher than 50 cm from the floor and no lower than 40 cm from the ceiling;
- There should be no fuel, lubricants or flammable substances and objects in the room;
- The base area in front of the ash pit is protected with metal sheet dimensions of at least 0.5x0.7 m.
In addition, at the location where the boiler is installed, an opening is provided for the chimney, which is led outside. Manufacturers indicate the configuration and dimensions of the chimney in the technical data sheet, so there is no need to invent anything. Of course, if the need arises, you can deviate from the documentation requirements, but in any case, the channel for removing combustion products must provide excellent traction in any weather. Installing chimney, all connections and cracks are sealed with sealing materials, and windows are also provided for cleaning the channels from soot and a condensate catcher.

Preparing to install a heating unit
Before installing the boiler, select a piping scheme, calculate the length and diameter of the pipelines, the number of radiators, type and quantity additional equipment and shut-off and control valves. Despite all the variety of design solutions, experts recommend choosing combined heating, which can provide forced and natural circulation of the coolant. Therefore, when making calculations, it is necessary to consider how a parallel section of the supply pipeline (bypass) with a centrifugal pump will be installed and to provide for the slopes necessary for the operation of the gravity system. You shouldn't give up either buffer tank. Of course, its installation will entail additional costs. However, a storage tank of this type will be able to level out the temperature curve, and one load of fuel will last for a longer time.

Particular comfort will be provided by a solid fuel boiler with an additional circuit, which is used for hot water supply. Considering the fact that due to the installation of a solid fuel unit in a separate room, the length of the DHW circuit, an additional circulation pump is mounted on it. This will eliminate the need to drain cold water while waiting for hot water to flow. Before installing the boiler, be sure to provide space for the expansion tank and not forget about devices designed to reduce pressure in the system in critical situations. A simple strapping diagram that can be used as a working design is shown in our drawing. It combines all the equipment discussed above and ensures its correct and trouble-free operation.
Installation and connection of a solid fuel heat generator
After carrying out all the necessary calculations and preparing the equipment and materials, installation begins.
- The heating unit is installed in place, leveled and secured, after which the chimney is connected to it.
- Heating radiators are mounted, a heat accumulator and an expansion tank are installed.
- Install the supply pipeline and bypass, on which the circulation pump is installed. In both sections (direct and bypass) install Ball Valves so that the coolant can be transported by forced or in a natural way. We remind you that the centrifugal pump can only be installed with the correct orientation of the shaft, which must be in a horizontal plane. The manufacturer indicates diagrams of all possible installation options in the product instructions.
- The pressure line is connected to the heat accumulator. It must be said that both the inlet and outlet pipes of the buffer tank must be installed in its upper part. Thanks to this, the amount of warm water in the container will not affect the readiness heating circuit. We definitely note the fact that cooling the boiler during the reboot period will reduce the temperature in the system. This is due to the fact that at this time the heat generator will work as an air heat exchanger, transferring heat from the heating system to the chimney. To eliminate this shortcoming, separate circulation pumps are installed in the boiler and heating circuits. By placing a thermocouple in the combustion zone, you can stop the movement of coolant through the boiler circuit when the fire dies out.

- A safety valve and an air vent are installed on the supply line.
- Connect the emergency circuit of the boiler or install shut-off and control valves, which, when the water boils, will open the main line for its discharge into the sewer and the channel for supplying cold liquid from the water supply.
- Install a return pipeline from the heat accumulator to the heating unit. A circulation pump, a three-way valve and a settling filter are installed in front of the boiler inlet pipe.
- An expansion tank is mounted separately on the return pipeline. Note! Shut-off valves are not installed on pipelines that are connected to protection devices. These areas should have as few connections as possible.
- The upper outlet of the heat storage tank is connected to a three-way valve and the circulation pump of the heating circuit, after which the radiators are connected and the return pipeline is installed.
- After connecting the main circuits, they begin to install a hot water supply system. If the heat exchanger coil is built into the boiler, then it will be enough to simply connect the cold water inlet and the outlet to the “hot” line to the appropriate pipes. When installing a separate indirect heating water heater, use a circuit with an additional circulation pump or three-way valve. In both cases, a check valve. It will block the path for heated liquid into the “cold” water supply.
- Some solid fuel boilers are equipped with a draft regulator, the function of which is to reduce the flow area of the blower. Due to this, the air flow into the combustion zone is reduced and its intensity, and, accordingly, the temperature of the coolant is reduced. If the heating unit has this design, then install and adjust the drive of the air damper mechanism.
The places of all threaded connections must be carefully sealed using plumbing flax and a special non-drying paste. After installation is completed, coolant is poured into the system and turned on at full power. centrifugal pumps and carefully inspect all connections for leaks. After making sure that there are no leaks, fire up the boiler and check the operation of all circuits at maximum modes.
Features of integrating a solid fuel unit into an open heating system
The main feature of open heating systems is the contact of the coolant with atmospheric air which occurs with the participation of the expansion tank. This container is designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant that occurs when it is heated. The expander is installed at the highest point of the system, and in order to prevent hot liquid from flooding the room when the tank is overfilled, a drain tube is connected to its upper part, the other end of which is discharged into the sewer.

The large volume of the tank forces it to be installed in the attic, so you will need additional insulation expander and tubes suitable for it, otherwise they may freeze in winter. In addition, you must remember that this element is part of the heating system, so its heat losses will lead to a decrease in the temperature in the radiators. Since the open system is not sealed, there is no need to install a safety valve or connect emergency circuits. When the coolant boils, the pressure will be released through the expansion tank.
Special attention should be paid to pipelines. Since the water in them will flow by gravity, the circulation will be influenced by the diameter of the pipes and the hydraulic resistance in the system. The last factor depends on turns, narrowings, level changes, etc., so their number should be minimal. In order to initially impart the necessary potential energy to the water flow, a vertical riser is installed at the outlet of the boiler. The higher the water can rise along it, the higher the coolant speed will be and the faster the radiators will warm up. For the same purposes, the return inlet should be located at the lowest point of the heating system.
Finally, I would like to note that in open systems It is preferable to use water rather than antifreeze. This is due to higher viscosity, reduced heat capacity and rapid aging of the substance upon contact with air. As for the water, it is best to soften it and, if possible, never drain it. This will increase the service life of pipelines, radiators, heat generators and other heating equipment several times.
 Solid fuel boiler piping - Emergency cooling valve
Solid fuel boiler piping - Emergency cooling valve
3. Protection against low temperature of the coolant in the “return” of the solid fuel boiler.
What will happen to a solid fuel boiler if its return temperature is below 50 °C? The answer is simple - a tarry coating will appear on the entire surface of the heat exchanger. This phenomenon will reduce the performance of your boiler, make it much more difficult to clean, and most importantly, can lead to chemical damage to the walls of the boiler heat exchanger. To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to provide appropriate equipment when installing a heating system with a solid fuel boiler.
The task is to ensure the temperature of the coolant that returns to the boiler from the heating system at a level not lower than 50 °C. It is at this temperature that the water vapor contained in the flue gases of a solid fuel boiler begins to condense on the walls of the heat exchanger (transition from a gaseous state to a liquid one). The transition temperature is called the “dew point”. The condensation temperature directly depends on the moisture content of the fuel and the amount of hydrogen and sulfur formations in the combustion products. As a result of a chemical reaction, iron sulfate is obtained - a substance useful in many industries, but not in a solid fuel boiler. Therefore, it is quite natural that manufacturers of many solid fuel boilers remove the boiler from warranty if there is no heating system return water. After all, here we are not dealing with the burning of metal at high temperatures, but with chemical reactions, under which no boiler steel can withstand.
The simplest solution to the problem of low return temperature is to use a thermal three-way valve (anti-condensation thermostatic mixing valve). The thermal anti-condensation valve is a thermomechanical three-way valve that ensures the admixture of coolant between the primary (boiler) circuit and the coolant from the heating system in order to achieve a fixed boiler water temperature. In essence, the valve releases the coolant that has not yet been heated in a small circle and the boiler heats itself. After reaching the set temperature, the valve automatically opens the coolant to the heating system and operates until the return temperature again drops below the set values.
 Solid fuel boiler piping - Anti-condensation valve
Solid fuel boiler piping - Anti-condensation valve
4. Protection of the heating system of a solid fuel boiler from operation without coolant.
Operating a boiler without coolant is strictly prohibited by all manufacturers of solid fuel boilers. Moreover, the coolant in the heating system must always be under a certain pressure, which depends on your heating system. When the pressure in the system drops, the user opens the tap and fills the system to a certain pressure.
IN in this case There is a “human factor” that may well make mistakes. This issue can be resolved using automation.
Automatic make-up installation is a device that is adjusted to a certain pressure and connected to an open water tap. If the pressure drops, the process of filling the system to the required pressure will occur fully automatically.
In order for everything to work correctly, it is necessary to fulfill certain conditions when installing the automatic refill valve:
- the automatic make-up valve must be installed at the lowest point of the heating system;
- during installation, it is necessary to leave access for cleaning or possible replacement of the valve;
- water from the water supply must be constantly supplied to the valve with pressure, and the water supply tap and the make-up valve must always be open.
 Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic feed valve
Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic feed valve
5. Removing air from the heating system of a solid fuel boiler.
Air in the heating system can cause a number of problems: poor circulation of coolant or its absence, noise during pump operation, corrosion of radiators or heating system elements. To avoid this, it is necessary to bleed the air from the system. There are two ways to do this - the first is manually - we are thinking about installing cranes in highest point systems and in lifting areas and periodically go through these taps, releasing air. The second way is to install an automatic air release valve. The principle of its operation is simple - when there is no air in the system, the valve is filled with water and the float is located at the top of the valve, and, through a hinged lever, seals the air outlet valve.
When air enters the valve chamber, the water level in the valve drops, the float lowers and, through a hinged lever, opens the air release hole on the outlet valve. As air leaves the chamber, the water level rises and the valve returns to the upper position.
We have already described the design of the boiler safety group above when we talked about protection against high coolant pressure. Ideally, if you have installed a safety group, it has an automatic air release valve. Just make sure that the safety group is installed at the top of your heating system. If not, we recommend installing a separate automatic air release valve and forever solving the problem of finding air pockets in your heating system.
 Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic air release valve
Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic air release valve
After installing the heating system, it is necessary to adjust the temperature regime. This procedure must be carried out in accordance with existing standards.
The coolant temperature requirements are set out in regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems residential and public buildings. They are described in the State Building Codes and Rules:
- DBN (V. 2.5-39 Heat networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning.”
For the calculated supply water temperature, the figure is taken that is equal to the water temperature at the outlet of the boiler, according to its passport data.
For individual heating, deciding what the coolant temperature should be should take into account the following factors:
- The beginning and end of the heating season based on the average daily outdoor temperature of +8 °C for 3 days;
- The average temperature inside heated premises of housing, communal and public importance should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16°C;
- The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” (clause 3.20), the coolant limit values are as follows:

Depending on the external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 °C, dust and paintwork begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit greater heating.
To calculate optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, which define standards depending on the season:
- With an average reading outside the window of 0 °C, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at 40 to 45 °C, and the return temperature at 35 to 38 °C;
- At -20 °C, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °C, and the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °C;
- At -40 °C outside the window, all heating devices are set to the maximum permissible values. On the supply side it is from 95 to 105 °C, and on the return side it is 70 °C.
Optimal values in an individual heating system
H2_2Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of standards includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is ensured design features heating devices.
It is important to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. The optimal temperature is considered to be 80 °C. With a gas boiler, it is easier to control heating, because manufacturers limit the ability to heat the coolant to 90 °C. Using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
It is a little more difficult with solid fuel devices; they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And it is impossible to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob in such a situation. Control of heating of the coolant is quite conditional with high errors and is carried out by rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Electric boilers allow you to smoothly regulate the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 °C. They are equipped with an excellent overheat protection system.
Single-pipe and double-pipe lines
The design features of one-pipe and two-pipe heating networks determine different standards for heating the coolant.
For example, for a single-pipe main the maximum norm is 105 °C, and for a two-pipe main it is 95 °C, while the difference between the return and supply should be respectively: 105 - 70 °C and 95 - 70 °C.
Coordination of coolant and boiler temperatures
 Regulators help coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler. These are devices that create automatic control and adjustment of return and supply temperatures.
Regulators help coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler. These are devices that create automatic control and adjustment of return and supply temperatures.
The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it. Regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between the return and supply to the level required, and the necessary indicators are installed on the sensor.
If the flow needs to be increased, a boost pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transported from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows according to the data collected by the sensor, and ensures strict temperature standards for the heating network.
Ways to reduce heat loss
 The above information will help to be used to correctly calculate the coolant temperature norm and tell you how to determine situations when you need to use a regulator.
The above information will help to be used to correctly calculate the coolant temperature norm and tell you how to determine situations when you need to use a regulator.
But it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is affected not only by the temperature of the coolant, street air and wind strength. The degree of insulation of the facade, doors and windows in the house should also be taken into account.
To reduce heat loss from your home, you need to worry about its maximum thermal insulation. Insulated walls, sealed doors, and metal-plastic windows will help reduce heat loss. This will also reduce heating costs.
At the supply it is from 95 to 105 °C, and at the return - 70 °C. Optimal values in an individual heating system H2_2 Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of standards includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is ensured by the design features of the heating devices. It is important to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. The optimal temperature is considered to be 80 °C. With a gas boiler, it is easier to control heating, because manufacturers limit the ability to heat the coolant to 90 °C. Using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
Coolant temperature in different heating systems
It, in turn, depends on what minimum and maximum water temperatures in the heating system can be achieved during operation. Measuring the temperature of a heating battery For autonomous heating, the standards are quite applicable central heating. They are set out in detail in Resolution of the PRF No. 354. It is noteworthy that the minimum water temperature in the heating system is not indicated there.
It is only important to observe the degree of heating of the air in the room. Therefore, in principle, the operating temperature of one system may be different from another. It all depends on the influencing factors mentioned above.
In order to determine what temperature should be in the heating pipes, you should familiarize yourself with the current standards. Their contents include a division into residential and non-residential premises, as well as the dependence of the degree of air heating on the time of day:
- In the rooms during the daytime.
Norms and optimal values of coolant temperature
Info
Over time, the maximum water temperature in the heating system will lead to breakdown. Also, a violation of the water temperature schedule in the system autonomous heating provokes the formation air jams. This occurs due to the transition of the coolant from liquid to gaseous state. Additionally, this affects the formation of corrosion on the surface of the metal components of the system.
Attention
That is why it is necessary to accurately calculate what temperature should be in the heat supply batteries, taking into account their material of manufacture. Most often, a violation of the thermal operating conditions is observed in solid fuel boilers. This is due to the problem of adjusting their power. When a critical temperature level in the heating pipes is reached, it is difficult to quickly reduce the boiler power.
Heating in a private house. there are doubts about the correctness of the system made.
For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit greater heating. To calculate optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, which define standards depending on the season:
- With an average reading outside the window of 0 °C, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at 40 to 45 °C, and the return temperature at 35 to 38 °C;
- At -20 °C, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °C, and the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °C;
- At -40 °C outside the window, all heating devices are set to the maximum permissible values.
Coolant temperature in the heating system: calculation and regulation
According to regulatory documents, the temperature in residential buildings should not fall below 18 degrees, and for children's institutions and hospitals it is 21 degrees Celsius. But it should be taken into account that depending on the air temperature outside the building, the building through the enclosing structures may lose different amounts of heat. Therefore, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system, based on external factors, varies from 30 to 90 degrees.
When heating water above heating structure decomposition begins paint coatings what is prohibited sanitary standards. To determine what the temperature of the coolant in the batteries should be, specially developed temperature charts are used for specific groups of buildings. They reflect the dependence of the degree of heating of the coolant on the state of the outside air.
Heating system water temperature
- In the corner room +20°C;
- In the kitchen +18°C;
- In the bathroom +25°C;
- In corridors and stairwells +16°C;
- In the elevator +5°C;
- In the basement +4°C;
- In the attic +4°C.
It should be taken into account that these temperature standards refer to the heating season and do not apply to the rest of the time. Also, it will be useful to know that hot water should be from +50°C to +70°C, according to SNiP-u 2.08.01.89 “Residential buildings”. There are several types of heating systems: Contents
- 1 With natural circulation
- 2 With forced circulation
- 3 Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device
- 3.1 Cast iron radiators
- 3.2 Aluminum radiators
- 3.3 Steel radiators
- 3.4 Warm floor
With natural circulation The coolant circulates without interruption.
Optimal water temperature in a gas boiler
Usually a lattice fence is installed that does not impede air circulation. Cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic devices are common. Consumer choice: cast iron or aluminum Aesthetics cast iron radiators- the talk of the town.
They require periodic painting, as the rules stipulate that working surface The heating device had a smooth surface and made it easy to remove dust and dirt. A dirty coating forms on the rough inner surface of the sections, which reduces the heat transfer of the device. But technical specifications cast iron products at height:
- are slightly susceptible to water corrosion and can be used for more than 45 years;
- have high thermal power per section, therefore they are compact;
- are inert in heat transfer, so they smooth out temperature changes in the room well.
Another type of radiator is made of aluminum.
A single-pipe heating system can be vertical or horizontal. In both cases, air pockets appear in the system. The system inlet temperature is maintained at a high temperature to warm all rooms, so pipe system must withstand high water pressure. Two-pipe system heating The principle of operation is to connect each heating device to the supply and return pipelines. The cooled coolant is sent through the return pipeline to the boiler. Additional investments will be required during installation, but there will be no air pockets in the system. Standards temperature regime for premises In a residential building the temperature is within corner rooms should not be below 20 degrees, for interior spaces The standard is 18 degrees, for showers - 25 degrees.
Standard coolant temperature in the heating system
Heating the stairwell Since we're talking about apartment building, then it should be mentioned staircases. The coolant temperature standards in the heating system state: the degree measure at the sites should not fall below 12 °C. Of course, the discipline of residents requires closing the entrance doors tightly, not leaving the transoms of the staircase windows open, keeping the glass intact and promptly reporting any problems to the management company.
If the management company does not take timely measures to insulate points of probable heat loss and maintain temperature conditions in the house, an application for recalculation of the cost of services will help. Changes in the heating design Replacement of existing heating devices in the apartment is carried out with the obligatory approval of management company. Unauthorized changes in the elements of warming radiation can disrupt the thermal and hydraulic balance of the structure.
Optimal coolant temperature in a private house
Consists of this device, shown in the photo, from the following elements:
- computing and switching node;
- working mechanism on the hot coolant supply pipe;
- an executive unit designed to mix in the coolant coming from the return. In some cases, a three-way valve is installed;
- booster pump at the supply section;
- The booster pump is not always in the “cold bypass” section;
- sensor on the coolant supply line;
- valves and shut-off valves;
- return sensor;
- outside air temperature sensor;
- several room temperature sensors.
Now you need to understand how the coolant temperature is regulated and how the regulator functions.
Optimal coolant temperature in the heating system of a private house
If the water temperature in the heating system of a private home exceeds the norm, the following situations may occur:
- Damage to pipelines. This is especially true for polymer lines, where the maximum heating can be +85°C. That is why the normal temperature of heating pipes in an apartment is usually +70°C.
Otherwise, deformation of the line may occur and a gust may occur;
- Excessive air heating. If the temperature of the heating radiators in the apartment provokes an increase in the degree of air heating above +27°C, this is outside the normal limits;
- Reduced service life of heating components. This applies to both radiators and pipes.
A heating boiler is a device that uses the combustion of fuel (or electricity) to heat the coolant.
Device (design) of a heating boiler: heat exchanger, heat-insulated housing, hydraulic unit, as well as safety elements and automation for control and monitoring. Gas and diesel boilers have a burner in their design, while solid fuel boilers have a firebox for wood or coal. Such boilers require a chimney connection to remove combustion products. Electric boilers are equipped with heating elements and do not have burners or a chimney. Many modern boilers are equipped with built-in pumps for forced circulation water.
Operating principle of a heating boiler- the coolant, passing through the heat exchanger, heats up and then circulates through the heating system, releasing the resulting thermal energy through radiators, heated floors, heated towel rails, as well as by heating water in an indirect heating boiler (if it is connected to the boiler).
A heat exchanger is a metal container in which the coolant (water or antifreeze) is heated - can be made of steel, cast iron, copper, etc. Cast iron heat exchangers are resistant to corrosion and quite durable, but are sensitive to sudden temperature changes and have heavy weight. Steel ones can suffer from rust, so they internal surfaces To increase the service life, they are protected with various anti-corrosion coatings. Such heat exchangers are the most common in the production of boilers. Copper heat exchangers are not susceptible to corrosion and, due to their high heat transfer coefficient, low weight and dimensions, such heat exchangers are popular and are often used in wall-mounted boilers, but usually more expensive than steel ones.
In addition to the heat exchanger, an important part of gas or liquid fuel boilers is the burner, which can be of various types: atmospheric or fan, single-stage or two-stage, with smooth modulation, double. ( Detailed description burners are presented in articles about gas and liquid fuel boilers).
To control the boiler, automation is used with various settings and functions (for example, a weather-dependent control system), as well as devices for remote control of the boiler - a GSM module (regulating the operation of the device via SMS messages).
The main technical characteristics of heating boilers are: boiler power, type of energy carrier, number of heating circuits, type of combustion chamber, type of burner, type of installation, presence of a pump, expansion tank, boiler automation, etc.
To determine required power heating boiler for a house or apartment, a simple formula is used - 1 kW of boiler power to heat 10 m 2 of a well-insulated room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m. Accordingly, if heating is required basement, glazed winter garden, rooms with non-standard ceilings, etc. The boiler power must be increased. It is also necessary to increase the power (about 20-50%) when providing a boiler and hot water supply (especially if it is necessary to heat the water in the pool).
Let us note a feature of calculating power for gas boilers: the nominal gas pressure at which the boiler operates at 100% of the power declared by the manufacturer for most boilers ranges from 13 to 20 mbar, and the actual pressure is gas networks in Russia it can be 10 mbar, and sometimes lower. Accordingly, a gas boiler often operates at only 2/3 of its capacity and this must be taken into account when calculating. When choosing the boiler power, be sure to note all the features of the thermal insulation of the house and premises. For more details, see the table for calculating the power of a heating boiler.
So which boiler is better to choose? Let's look at the types of boilers:
"Middle class"- average price, not so prestigious, but quite reliable, standard standard solutions. This Italian boilers Ariston, Hermann and Baxi, Swedish Electrolux, German Unitherm and boilers from Slovakia Protherm.
"Economy class"- budget options, simple models, service life is shorter than that of boilers of a higher category. Some manufacturers have budget boiler models, for example,