Weak heating boiler. The boiler does not heat to the set temperature
Change temperature regime heating operation can be caused by a number of internal causes. Many of them negatively affect the efficiency of the system, increasing energy costs. In such cases, a reasonable question arises - why does the heating not heat up: radiators, batteries, pumps, systems? The first step is to find the causes of the problem.
General heating problems
The principle of operation of any heating system is the efficient transfer of thermal energy from an energy carrier (gas, solid fuel, diesel, etc.) water in pipes. The task of heating devices (radiators, batteries, pipes) is to transfer the received heat to the room.
And if the heating battery does not heat up, the reasons for this may lie both in the design itself and in the parameters of the system as a whole. Consider the common reasons for the decrease in the efficiency of the heating system:
- Low efficiency of the boiler heat exchanger. Water is not heated to the desired temperature;
- A specific heating battery does not heat well. Possible reasons– incorrect installation, education air locks;
- Change specifications systems - an increase in hydrodynamic resistance in certain sections of the pipeline, a decrease in the passage diameter of pipes, etc. Most often, the consequence of such phenomena is very hot circulation pump heating.
In some cases, not one, but several of the listed problems occur. Often the main cause is the root cause of the appearance of the following. Thus, the formation of an air lock affects the increase in hydrodynamic resistance, and as a result, there is an increased load on the circulation pump.
Do not install decorative grilles or cover it with a panel on a radiator with poor heating. Thus, even so, the small efficiency of its work will be artificially reduced.
The radiator does not heat up
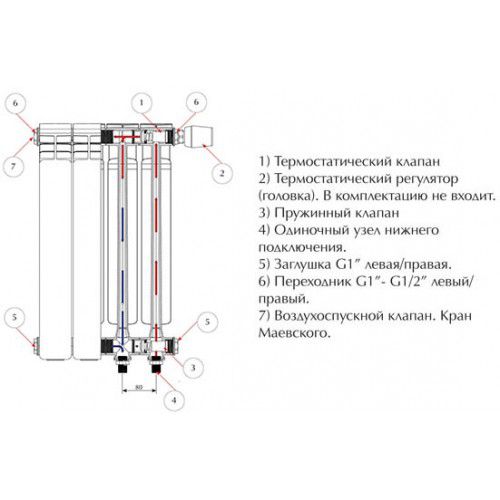
Most often, problems with normal heat transfer occur in heating radiators. This is due to their specific design - the coolant does not move through one pipe, as in the transport line, but is distributed over several.
In what cases does the heating radiator not heat up? There are several factors that directly affect the correct operation of the battery.
Air pockets in heating

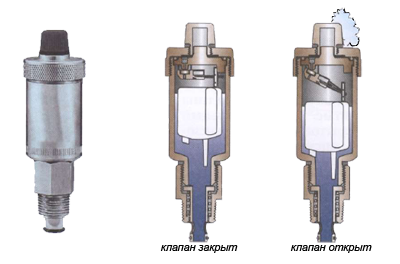
There are several reasons for the appearance - exceeding the temperature regime, evaporation of water, etc. It is important that the consequence of this is the appearance of places in the line that are not filled with coolant. Most often these are radiators. To eliminate them, it is necessary to install a Mayevsky crane - air valve, releasing excess air from the device.
How to determine why the heating radiator does not heat well? The simplest method is the temperature difference on the surface. At the place of formation of an air lock, it will be much lower, thereby preventing the normal passage of the coolant. To fix it, follow these steps:
- With the help of a screwdriver or a rotary lever, the Mayevsky tap is opened;
- Add water to the system until the coolant begins to flow out of the tap together with air;
- Shut off the water supply.
After the surface of the radiator should heat evenly. Otherwise, repeat the procedure.
For normal heating of the heating radiator, you need to install an adjusting thermostat. Depending on the set temperature mode, it will automatically adjust the volume of the coolant.
Incorrect installation and limescale in pipes
The efficiency of its operation depends on the correct installation of the radiator. It should not be inclined relative to the plane of the floor and wall. If this condition has not been met, then the question will inevitably arise - why the heating battery does not heat up.
To check the correct installation of the radiator, you can take a standard building level. If the upper plane of the battery has deviations, re-installation should be performed. It is best to use new reinforced mounts for this.
If, after this, the question of why the heating radiator does not heat up remains unresolved, it is recommended to flush the heating system. This problem is relevant for old pipes and radiators made of steel and cast iron. Over time on inner surface a lime layer accumulates, preventing the normal flow of the coolant. There are several ways to perform the flushing procedure:
- Hydraulic. A special pump is connected to the system circuit, which creates a large pressure of water. Under the influence of this force, the scale is broken into small fractions and retained in the pump filter;
- Chemical. Special additives act on limescale, which loses its uniformity and flakes off the inner surface. Subsequently, hydraulic flushing is performed to remove residual debris.
Experts recommend using an integrated method to solve the problem in which the heating battery does not heat up. After checking the correctness of the installation, the system is flushed, and then the correct filling is performed with the Mayevsky tap open.
If two-pipe heating system does not heat due to clogged pipes - you need to carefully choose the cleaning technology. For pipelines made of polypropylene, chemical cleaning cannot be done.
The boiler does not heat the batteries

Often, a two-pipe heating system does not heat due to the low heat transfer rate of the boiler exchange circuit. This leads to a decrease in the temperature regime and, as a result, a loss in the efficiency of the entire system. Not every boiler model provides for an easy way to dismantle the heat exchanger. If the heating does not heat well due to the appearance of plaque on the internal elements of the boiler, you can flush without this procedure. To do this, you need a pump with a filtration system. The procedure for cleaning is as follows:
- Switching off the boiler common system heating;
- Connection to the inlet and outlet pipe of the pump hoses;
- Filling a special cleaning liquid into the boiler heat exchanger;
- By using centrifugal pump the rate of passage of liquid through the boiler increases.
After that, the heating batteries should not heat up badly. Special attention should be given to the flushing liquid. It must not harm the metal elements of the boiler and the system. Therefore, at the end of the procedure, rinse the entire system with distilled water.
To avoid the appearance of scale, before pouring water into the heating system, it is necessary to reduce its hardness index. Usage running water not recommended as it contains a large number of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium. They are the main source of lime scale not only in the boiler heat exchanger, but also in pipes and radiators.
The best way to clean the heat exchanger is to dismantle it. So you can not only remove the entire amount of scale, but also make sure its integrity. After this procedure, the heating system should not heat up badly.
Pipelines: causes of low heating

Failures in the heating mode are characteristic two-pipe system heating. In this case, the supply line does not heat, distributing the coolant to the radiators. Identification of the "problem" zone can be done by measuring the temperature on the surface of pipes or a thermal imager.
natural circulation

What could be causing such problems? If the heating does not heat well, it is possible that the slope of the main line is not observed. This only applies to systems with natural circulation. According to the standards, the slope of the pipes should be 10 mm per 1 r.m. In addition, the direction is taken into account - from the accelerating riser to the radiators. For the return pipe, the slope must be towards the boiler.
At the first stage, it is necessary to measure this indicator using the building level. If it corresponds to the norm, but the heating radiator does not heat, there is a possibility of air locks. In this case, an integrated approach is recommended, which includes the following steps:
- Tilt angle measurement. If necessary, change it to the required indicator;
- Flushing pipes to remove limescale;
- Filling the system with coolant with open Mayevsky taps on radiators.
This technique will eliminate the low rate of heat transfer of the heating system.
To improve circulation in open systems you can install a circulation pump. If it overheats, you need to mount an additional one. This is often necessary for branched heating systems.
Forced coolant circulation
For a system with forced movement of water in the pipes, the formation of air pockets can be avoided by using an air vent installed at the top of the system. In part, it performs the functions of an open expansion tank, but at the same time does not reduce the pressure in the pipes to a critical level. Its absence is an indirect reason poor heating heating radiator.
The specificity of closed heating systems lies in the optional observance of the level of pipe installation. However, when the critical level of heating of the coolant is exceeded, steam is released, which is the main cause of air locks. Since air has a lower density than water, it will concentrate in the upper region of the pipeline sections. If the heating radiators do not heat well in closed system- the reason may be a decrease in the volume of coolant in the pipes due to air resistance.
What needs to be done in this case? First of all - check the performance of the air vents. If idle for a long time, the valve may become covered limescale which makes it impossible to open it under air pressure.
In addition to this factor, it is necessary to take into account the excess of hydraulic resistance in the system. That is why the battery in heating does not heat up if the initial calculation is wrong. Therefore, before proceeding with the installation new system or modernization of the old one - the calculated part of the operational and technical parameters should be performed.
Dear Sirs!! Just tormented with heating. I will accept any advice and help. Thanks in advance.
Problem status:
1. When the coolant is heated (the pressure in the system is about 1 atm, the characteristics of the Grundfos UPS 25-80 180 mm 2 stage pump) the nearby circuits are gradually heated, the temperature in the boiler rises, but latest batteries still stay cold.
2. At some point, the nearby circuits also stop heating, and all the batteries become cold, and the boiler boils.
3. Further, I achieve the desired result in different ways: I feverishly twist the central plug in the pump, releasing steam and coolant, turn the pump on and off, the last time it all lasted more than 2 hours, the process is generally uncontrollable. It seems that the pump works for itself and does not pump anything, I do everything at random.
4. Then at some point, everything suddenly breaks through, the batteries ALL instantly become hot, and the temperature in the boiler drops to 60 degrees. Further, everything can remain and work well for several hours, or again after 2-3 hours the batteries can cool down and the temperature in the boiler rises.
Heating scheme
Unfortunately, you did not indicate whether this was the first launch after installation, or whether the heating system worked successfully before. We will assume that the design and installation were carried out correctly, the capacity of the compensation tank and the sections of pipelines were chosen correctly. The floor-by-floor wiring diagram you sent is simple and should ensure satisfactory circulation of the coolant. By the way, connecting a radiator on a ladder to a vertical line is irrational, right decision it would be to connect after the riser.
There may be several reasons for the fact that the temperature of the coolant periodically rises to a critical level, and the radiators remain cold:
Most often, such problems are created by a “plug”, air or mud. Air is especially actively released in the first month after filling the system; it is recommended to bleed it daily. An air blower (Mayevsky crane) should be installed on each heater. Automatic air vents are mounted at the upper points of the heating mains, in the boiler room, on the boiler itself, on the collectors (you, judging by the diagram, do not have them). Airing the system is the most common cause unstable heating operation. We recommend that you start the test with a thorough deflation, first at the top, moving down. If the air has to be bled often, and the pressure in the system drops, the tightness is broken somewhere.

An air blower should be installed on each heating radiator
A mud “plug” can also interfere with the free flow of the coolant. The first step is to check the filter, if any. Also, air vents, especially needle-shaped ones (Maevsky taps), can also clog dirt and sludge.

Such a device combines the functions of an automatic air blower and a mud filter. Easy to maintain, allows you to ensure cleanliness and normal gas composition coolant
The reasons for the unstable operation of the heating may also lie in your circulation pump. Although, more often it fails immediately and permanently. Whether the pump is working can be checked by placing a hand on the body. A slight vibration should be felt. To begin with, we recommend checking and cleaning the electrical contacts. The reason may lie in the wear of parts of the electric motor or in the formation lime deposits if untreated tap water is used as the heat carrier.
Theoretically, it is possible to unscrew the plug on a non-working pump and carefully turn the shaft with a screwdriver, it often helps (temporarily). You can get rid of deposits by dismantling the pump and washing it for a day in vinegar or a solution citric acid. But still, it is not easy to disassemble and maintain the circulation pump without having the skill. By the way, outside the heating period, the pump, in order to avoid oxidation electrical connections and shaft lock, should not be idle. Once every two to three weeks, it is recommended to turn it on for 15 minutes.

After long downtime an air pocket may form in the pump. Before turning it on, check for required pressure in the system and vent not only the radiators, but also the pump itself
Rare, but still possible malfunctions in the electronics. Since the operation of the pump is controlled by the heating boiler controller, a failure in the program or incorrect operation of the sensors can adversely affect the operation of the system.




















