Two-pipe with top wiring. Upper and lower wiring of the heating system
Top wiring heating system is that the supply pipeline is located in the attic or under the ceiling. From the supply pipe, risers are laid down with pipes attached to them, which in turn are connected to heating appliances. The return line is laid on the floor or in the basement. Such a system of polypropylene pipes is an indisputable option for arranging a heating system without a circulation pump.
In other heating schemes, the circulation pump must be present without fail. In addition, when installing a heating system with wiring from above in the attic, it is necessary to install an expansion tank to protect the system from pressure drops, and an air vent.
The lower wiring is different in that the straight pipeline runs parallel to the return line along the floor of the first or ground floor or in the basement on the ceiling. Such wiring using polypropylene heating pipes It is used to organize the supply of coolant to each riser.
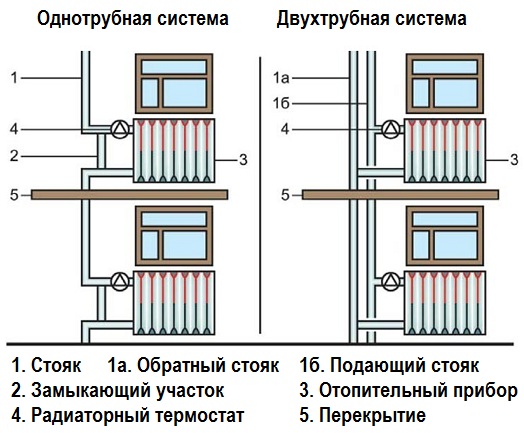
The heating system can be one- and two-pipe, if you look at the number of pipelines extending from the main. When installing a one-pipe system, you need to know that in such a scheme, the pipe is connected in turn to each device in the system. Moreover, from one radiator to another, the further along the system, the coolant loses temperature. This system is used for large houses, where residential premises are first connected to heating, and then utility or utility rooms. 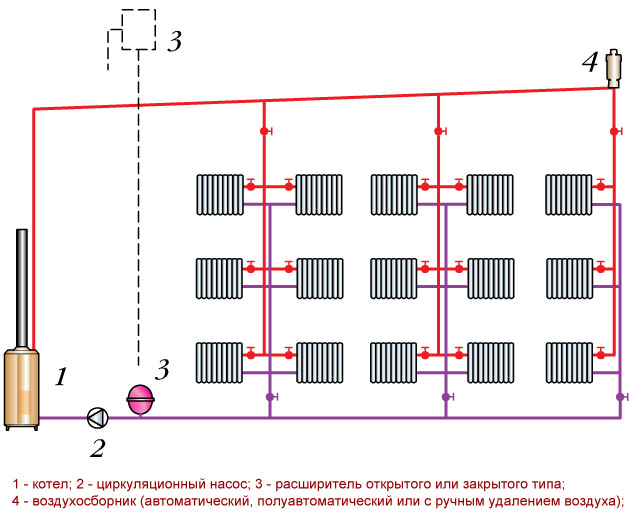
The two-pipe system is designed so that the hot stream and the already exhausted one go through different main pipelines - forward and reverse. In this case, a coolant with the same temperature will be delivered to each radiator. Big Advantage two-pipe system heating systems connected to radiators polypropylene pipes in the fact that in the event of an emergency, you can turn off the problematic riser without depriving the entire house of heating.
Heating distribution in horizontal and vertical type
The vertical type of wiring is usually done in high-rise buildings, where the coolant must pass through the risers from floor to floor. With this system, it is possible to repair a separate riser without turning off the rest. 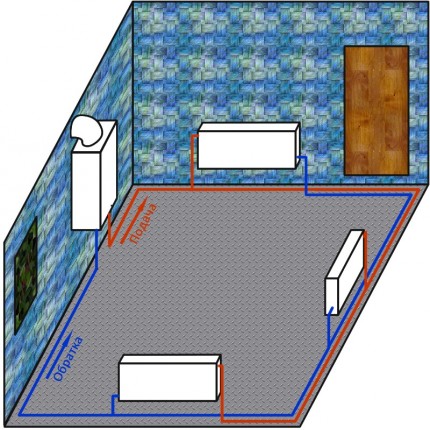
Horizontal wiring is the main riser and floor branching in one- and two-pipe versions. This scheme is more modern and is used in new apartment buildings, where each apartment has its own wiring.
In its turn horizontal type it is perimeter and radial.
Perimeter heating system
This system is connected to the central riser and the coolant moves sequentially through all radiator batteries located around the perimeter of the apartment or floor. This scheme has its drawbacks:
- when repairing one radiator, it is necessary to turn off the entire perimeter;
- it is difficult to drain the coolant, since the wiring is located at the same level horizontally.
Virtues perimeter system can be called an opportunity concealed installation highways in the floor. 
Collector-beam heating scheme
Similarly to the previous system, it is connected to the central riser. The main difference between such a scheme is the distribution of pipes in individual rooms, like rays to each radiator. A single piping system is formed in the collector near the riser. The disadvantages of this system are similar to those of the perimeter, and the advantages are the ability to turn off one heating branch without depriving others of their working capacity.
When choosing the optimal heating system, you should consider climatic conditions place of residence, the number of storeys of the room, the load on the heating devices separately, the possibility of an emergency shutdown.
Much easier and cheaper in the device, the two-pipe heating system of a private house does not lose its popularity.
This becomes possible only due to the few, but unique advantages that such structures possess.
Two highways - what is it
the biggest distinctive feature such schemes is the presence of two separate highways. The first is designed to deliver water to all heating elements, that is, radiators, and the second serves to collect cooled water and deliver it to heating element eg gas boiler.
If in a one-pipe design with forced or natural circulation the coolant partially cools down until it reaches each individual radiator, then in the case of a two-pipe system, this process is hardly noticeable.
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system has the following positive qualities:
- For the installation of such systems, pipeline elements with a large diameter are not required, since there will be practically no obstacles in the way of the coolant, which cannot be said about single pipe heating. Since thinner pipes are cheaper, the cost of the entire project will be less. You can also add here that smaller pipes will require smaller valves, fasteners and other shaped elements, which, of course, also cost less;
- It is possible to install thermostats near each heating radiator, which greatly increases the comfort of operation of such heating;
- It must be said that thinner pipes, fasteners and valves are not so “striking”, therefore they do not spoil the interior.
As for the shortcomings, one can be noted and, probably, the most relevant is the cost. In fact, it is not large, but in comparison with a single-pipe system, it is much larger. However, after evaluating all the pros and cons, for a private residential building, especially when it comes to multi-storey housing, the choice leans towards a two-main structure.
Classification
So, it should be noted right away that self-flowing schemes with two highways are rarely found. In fact, they should not be at all, since they are ineffective. If you are destined to meet such people anywhere, then only in very old houses.
It must be said that today all gas and electric boilers already have a pump in their design, so these designs are called with forced circulation.
Among other things, these types of heating can be:
- Horizontal;
- Vertical.
Both of them can be done by hand.

The division into these two categories is carried out according to the location of the pipeline. It must be said right away that there are no differences in the design itself, and the list of constituent elements is as follows:
- Riser;
- Heating elements, i.e. radiators;
- Shut-off valves on each of the radiators;
- Air bleed valve;
- Some elements of control valves;
- Direct highway;
- Return line;
- The heating element, i.e. the boiler.
Of course, the entire heating system with forced circulation, both with the lower wiring and with the upper one, may include other elements, but the main ones are listed here.
So everything vertical circuits have a characteristic structure in which all elements are attached to the riser.
Advice! Two-pipe or buildings with a large number of floors should be built exactly according to this principle, since such a design does not allow air cavities to form inside the pipeline.
Scheme with horizontal wiring suitable for houses and buildings that have one floor and a fairly large heating area. In this case, the connection will be much easier, and the cost is lower.
Bottom and top wiring
Among other things, the division is also carried out according to the method of laying the pipeline, that is, according to the method of installing the wiring. There are schemes:
- With bottom wiring;
- FROM top wiring.
Top wiring
The most important difference from the rest is that this species It has expansion tank, which is installed on the high point. In addition, this expansion tank must be located above all other elements.
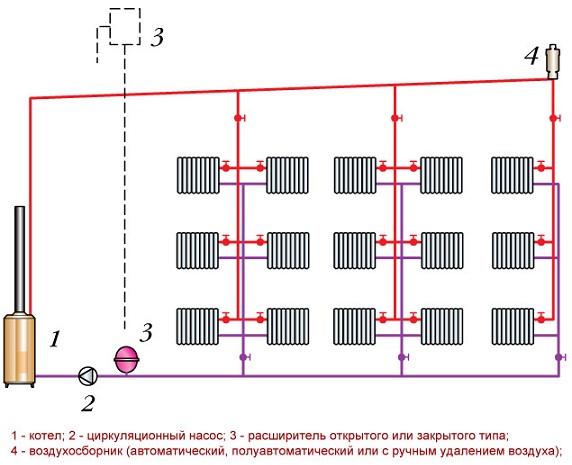
Structurally, such a system should contain the following elements:
- Heating boiler;
- Circulation pump;
- Expansion capacity;
- Air collector, which can be manual, automatic or semi-automatic.
Advice! Such structures should be assembled with your own hands only in a pre-insulated attic, or the expansion tank itself should be additionally insulated.
It should be noted that for a one-story building with a sloping roof, such a scheme is not suitable.
Bottom wiring
All systems with bottom wiring have the peculiarity that the supply line is usually located in basement. Often the supply and return lines are located on the floor.
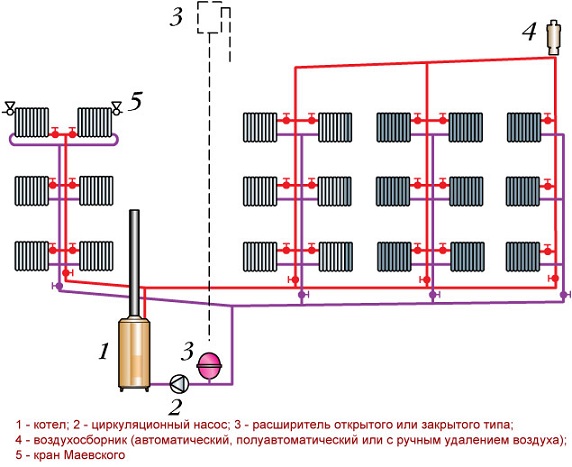
Structurally, this scheme will include the following elements:
- Heating boiler;
- Circulation pump;
- Expansion capacity;
- Air collector;
- Mayevsky crane.
I must say that regardless of where the supply pipes are located, the boiler must be located below the level of the return line.
The direction of movement of the coolant
Along with the above classification, all two-line heating systems with forced circulation are divided into the following types:
- Direct-flow;
- Dead end.
Direct-flow are characterized by the fact that both in the direct line and in the return, the liquid moves in one direction.
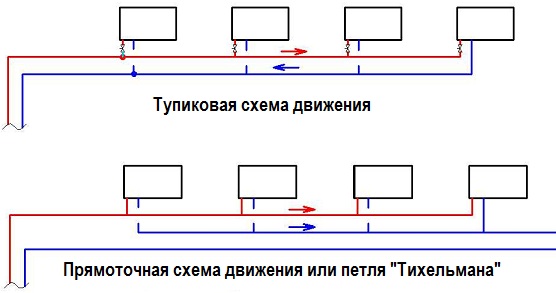
Dead ends have different directions movement of the coolant in different lines.
I must say that all such schemes, as noted earlier, in the vast majority of cases today are equipped with circulation pump. But the fundamental existence of circuits with a lower wiring with a natural movement of the coolant is possible. When constructing such structures, it is important to remember that the minimum slope of the pipeline should be 1 percent of the total length.
Basic rules for hydraulic calculation
Hydraulic calculation is necessary in order to correctly calculate the pressure loss in the system, determine the power of the heating boiler, determine the minimum required pipe diameter, the number of radiators and much more.
However, it is extremely difficult to make such a calculation without the appropriate knowledge, so we will consider only some of the rules for its implementation.
Hydraulic calculation is performed only according to a pre-compiled scheme.
The main object will, as a rule, be the most loaded ring, which is divided into several separate sections - hydraulic calculation is carried out on each of them.
It must be said that, depending on the desired value, the hydraulic calculation can be carried out in different ways, that is, it can have several types.
The most relevant for private construction can be considered the following:
- Hydraulic calculation by finding specific linear pressure losses;
- Finding the resistance of the system.
The first calculation shows the possible pressure loss in the system due to its imperfection, that is, the numerous turns of the pipeline, for example. The second one shows what kind of resistance to the flow of the coolant is provided by this or that obstacle.
No matter how different these calculations may seem, they have the same goal - to determine how various twists, roughness and other obstacles will affect the thermometer reading.
Unlike single pipe system, where common pipe and holds hot water on all radiators, and brings it back, a two-pipe heating system with an upper wiring, as well as a lower one, has separate circuits for supplying hot coolant and for diverting waste water back to the boiler. The advantage of such a scheme is that the coolant will not gradually lose heat, moving from battery to battery, the heating of the room will occur more evenly. The downsides are perhaps the higher cost and laboriousness of installation.
The design of a forced circulation heating system can be different, depending on the characteristics of a particular building.
Vertical and horizontal layouts
A double-circuit heating system with forced circulation may differ in the direction of installation of risers: vertical or horizontal. Two-pipe scheme The first type has the following advantages:
- Allows you to connect each floor two-story house to the riser separately;
- Vertical installation prevents air locks.
Minuses vertical wiring are limited only to the fact that the installation of a water heating system with your own hands has an increased cost.
The horizontal heating system of a private house is used more often in buildings with one floor. Radiators are connected to such a system in two ways:
- Beam or collector;
- Consistent.
At collector circuit connections, each radiator receives the coolant separately. The first type of system has everything heating appliances have a common pair heating circuits, which are combined by a collector box. The advantages of the first option are that there is no need to adjust the system with your own hands and control the patency stop valves, the temperature of the radiators will be the same throughout the system. However, the price of materials is higher due to the higher consumption of pipes. Series circuit connection is more simple and practical, allows you to easily adjust the temperature of the coolant.
Important! The installation of a beam system is justified only in one-story house. For a two-story house and more floors, it is better to choose a sequential scheme.
Top and bottom wiring
 The two-pipe system with the top wiring is always vertical, and the radiators in it are connected in parallel. In such a heating system of a two-story house, an expansion tank must be present, mounted at the top of the supply circuit. The pipes of both circuits should be installed with a slight deviation from the horizontal in the direction of the water flow. The system is fed with water through the pipes of the discharge circuit. Cold water mixes with the discharged coolant, increasing its density and increasing the circulation pressure in the heating system.
The two-pipe system with the top wiring is always vertical, and the radiators in it are connected in parallel. In such a heating system of a two-story house, an expansion tank must be present, mounted at the top of the supply circuit. The pipes of both circuits should be installed with a slight deviation from the horizontal in the direction of the water flow. The system is fed with water through the pipes of the discharge circuit. Cold water mixes with the discharged coolant, increasing its density and increasing the circulation pressure in the heating system.
The scheme of operation of the system with forced circulation is as follows: the pump drives the heated coolant to the attic of a two-story house, from where the water descends into the lower rooms along the supply circuit, entering the radiators. Having given up its heat in them, the water flows back into the boiler along the return pipe, the pipes of which are located below the level of installation of the batteries.
A two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring differs from the previous type in that the supply circuit is laid by hand next to the outlet pipes, water is supplied from below. Lower wiring is rarely used due to the fact that it has significant disadvantages. In a system with a lower wiring, the formation of air pockets is inevitable, which necessitates the supply of all final radiators with Mayevsky taps, through which air must be bled every week.
Dead-end and associated systems
 Heating systems with forced circulation may differ in the direction of the flow of the coolant. On this basis, the system is dead-end and straightforward:
Heating systems with forced circulation may differ in the direction of the flow of the coolant. On this basis, the system is dead-end and straightforward:
- With passing movement, the direction of the leading and reverse flows coincides;
- The dead-end circulation of the coolant assumes a multidirectional flow of water.
The system with bottom or top wiring can also be open or closed type. Their difference is that open system is flowing, supplied with hot coolant centrally or has a leaky circuit. AT closed system with forced circulation, heating of the coolant is applied in closed loop. The first scheme of a two-pipe system is usually used in multi-apartment and high-rise buildings, and the second is more suitable for a one- or two-story private house.
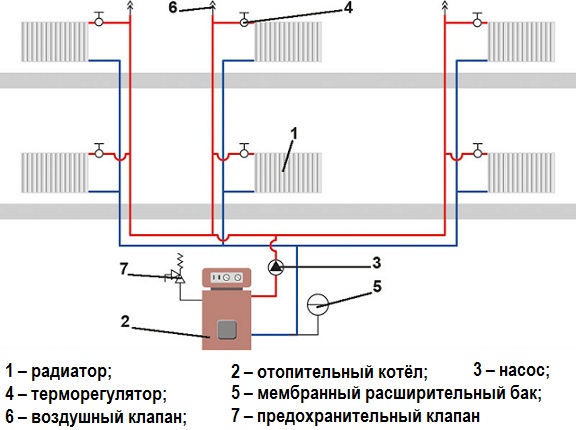
The double-circuit heating system with lower or upper wiring consists of the following elements:
- heating boiler;
- Radiators;
- Pipes and pipeline filter;
- expansion tank;
- Fittings for balancing - valves, taps, valves;
- Pump in the case of forced circulation;
- Groups of safety and pressure gauges.
Hydraulic calculation
H2_2Hydraulic calculation is carried out using a variety of methods, the most popular of which are:
- Calculation by indicators of specific pressure losses, which involves obtaining information on temperature fluctuations in all elements of the heating system and on the exact flow rate of the coolant;
- Calculation of a two-pipe heating system according to the resistance and conductivity of the circuits.
As a result, the hydraulic calculation provides information on the exact temperature characteristics of the heating system and on the flow of water in all areas, which allows you to get a picture of the distribution of heat throughout the room and plan optimal scheme heating of a two-story house.
Important! The collector part of the system must be calculated separately.
Do-it-yourself installation and balancing
 Double-circuit heating with forced circulation for a two-story house must be installed and adjusted in accordance with the following rules:
Double-circuit heating with forced circulation for a two-story house must be installed and adjusted in accordance with the following rules:
- The inlet circuit must be located above the outlet;
- The slope of the pipes towards the last radiator is from 0.5 to 1% of the entire length;
- The lower and upper contours should run symmetrically and parallel to each other;
- Connection of all elements of the system occurs with the equipment of their shutoff valves;
- The supply circuit must be covered with insulation to prevent heat loss;
- The contours are fastened in increments of 120 cm.
Installation of the heating system of a two-story house includes the installation of an expansion tank, a heating boiler, radiators and pipelines. When doing the installation yourself, you should consider:
- The supply circuit departs from the boiler, first it is connected to expansion tank, then pipe goes to radiators;
- In a system with forced circulation, the pump is installed as close as possible to the starting point, that is, at the outlet of the boiler room;
- The return circuit is mounted parallel to the supply pipeline, connected to all batteries and connected to the boiler;
- Radiators should be installed in compliance with optimal indents - about 10 cm from the floor and a few centimeters from the walls;
- Next to the radiators, shut-off valves and elements are installed, with the help of which the system is balanced.
If used collector system with lower wiring, all circuits are additionally connected by a collector pipe. Its diameter must not be less than the sum of the diameters of the nozzles included in it.
Balancing includes a test run of the system, air removal through Mayevsky taps, pressure and temperature checks. Setting optimal mode work is carried out according to temperature using cranes or balancing valves or according to the flow rate of the coolant, using electronic flow meters for this, the connection of which must be through balancing valves. You can more precisely adjust the temperature with your own hands using thermostats.



















